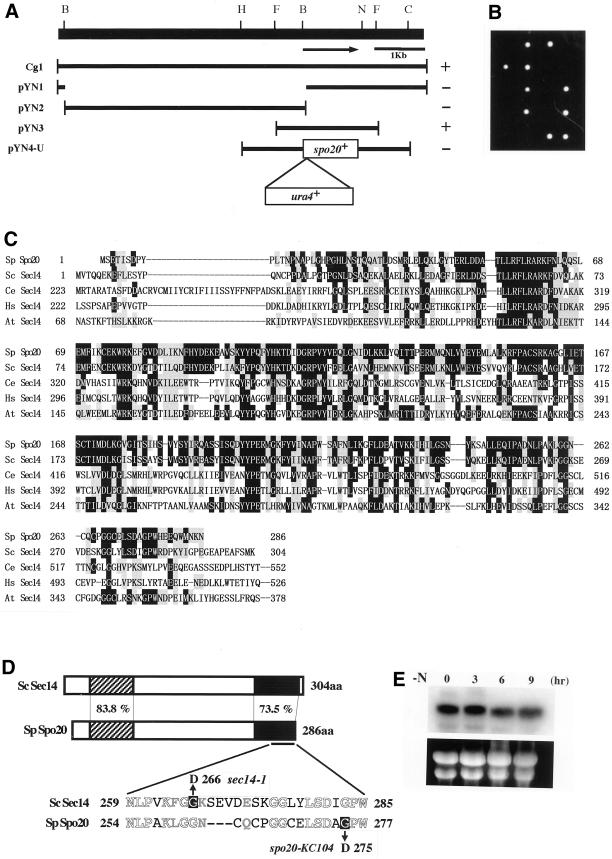
Figure 3.
Structure of the spo20+ gene. (A) Restriction map, subcloning, and construction of null mutants. The arrow indicates the region and direction of the spo20+ ORF, which encodes a protein composed of 286 amino acid residues. All the subclones were derived from Cg1. Complementation by each subclone: +, complements; −, does not complement. Restriction enzyme sites: B, BamHI; C, ClaI; F, FbaI; H, HindIII; N, NcoI. (B) Viability of spo20::ura4+ spores. A diploid (YN16) heterozygous at the spo20 locus (+/spo20::ura4+) was sporulated, and the dissected tetrads were incubated on YEA plates at 25°C for 5 d. (C) Comparison of the amino acid sequences of Spo20 and other members of the Sec14 family. Identical amino acids are shown in white against black, and similar amino acids are shaded. Sp, S. pombe (286 aa); Sc, S. cerevisiae (304 aa); Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans (743 aa); Hs, Homo sapiens (715 aa); At, Arabidopsis thaliana (648 aa). (D) Schematic representation of the structures of Spo20 and Sec14. The overall identity and similarity between Spo20 and Sec14 are 54.5 and 76.6%, respectively. The amino acid similarities between them in the N-terminal (hatched) and C-terminal (filled) conserved domains are also shown. The spo20-KC104 mutant allele carries a single nucleotide change (from G to A) that results in the replacement of glycine 275, as shown by white against black, with asparatate. For comparison, the mutation site of sec14-1ts is also shown (Cleves et al., 1989). Identical amino acids are represented by white letters, and similar amino acids are represented by gray ones. (E) Northern analysis. L968 precultured in growth medium (MM+N) was incubated in liquid sporulation medium (MM-N) at 25°C. After the shift, samples were taken and subjected to Northern blotting. Top, spo20+ mRNA; bottom, rRNA stained with ethidium bromide.