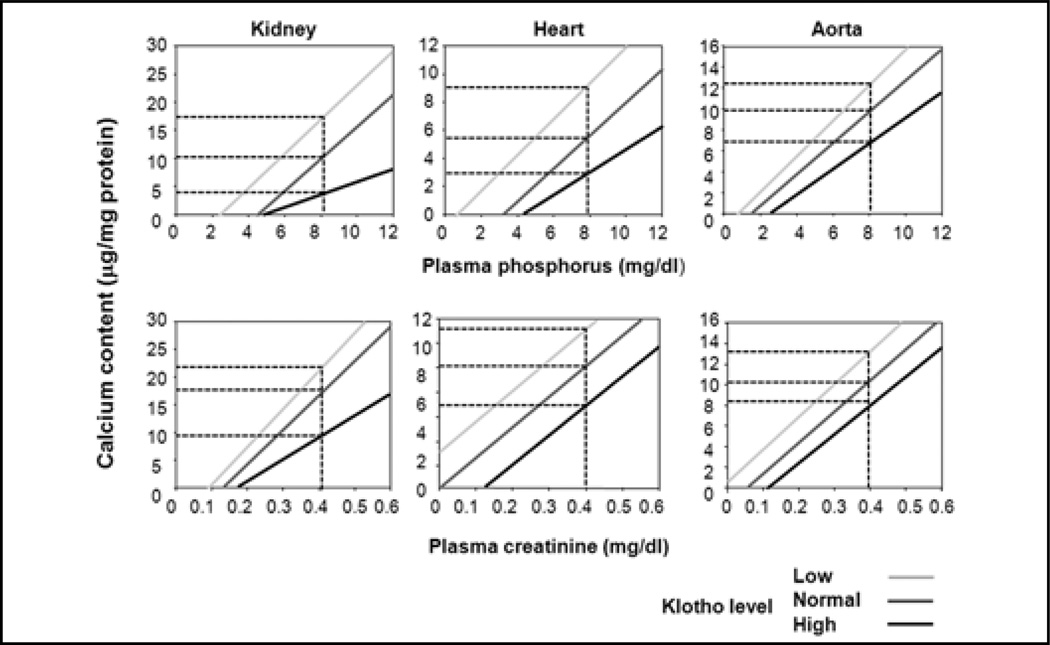
Fig. 4.
Correlation of calcium content in the kidneys, hearts and aortas in sham and chronic kidney disease (CKD) mice. Calcium content was assayed using o-cresolphthalein complexone (OCPC) in the kidney, heart and aortas of sham and CKD mice at different genetic Klotho levels: Kl+/− (light gray) and Tg-Kl (black gray) and their wild-type (WT) littermates (dark gray). For given concentration of blood creatinine (Cr) or phosphate (Pi) (vertical dotted line) Kl+/− (light gray) mice have the highest, and Tg-Kl (black) the lowest and their WT littermates (dark gray) intermediate levels of Ca content in soft tissues.