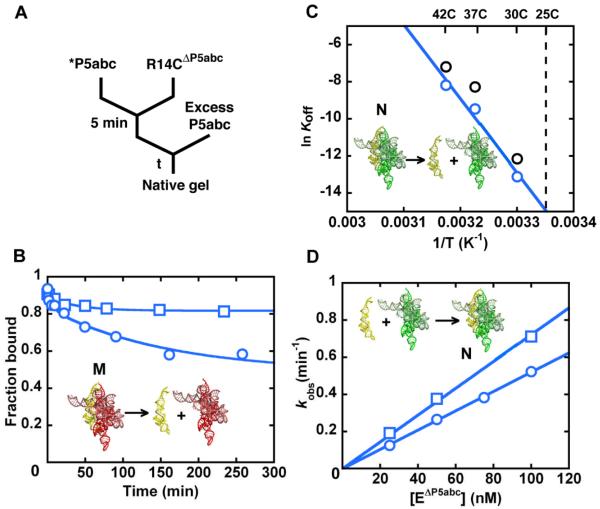
Figure 3.
Preferential binding of P5abc to the native R14CΔP5abc ribozyme. (A) To measure dissociation, radiolabeled P5abc (*P5abc) was allowed to bind to the ribozyme and then chased with unlabeled P5abc. (B) Dissociation kinetics of P5abc from a population of predominantly native R14CΔP5abc ribozyme (blue squares) or a mixture of native and misfolded R14CΔP5abc (blue circles). The mixture gave a major phase of dissociation with a rate constant of 0.0072 ± 0.0003 min−1, whereas most of the P5abc remained bound to the native ribozyme on the observable time scale (up to 5 days, additional data points not shown). (C) Determination of the rate constant for P5abc dissociation from the native R14CΔP5abc ribozyme by extrapolation from measurements at higher temperatures (blue). Data for the EΔP5abc ribozyme obtained side-by-side are shown in black and were consistent with previous results (21). (D) Association kinetics of P5abc to predominantly native R14CΔP5abc ribozyme (blue squares) or a mixture of native and misfolded R14CΔP5abc ribozyme (blue circles).