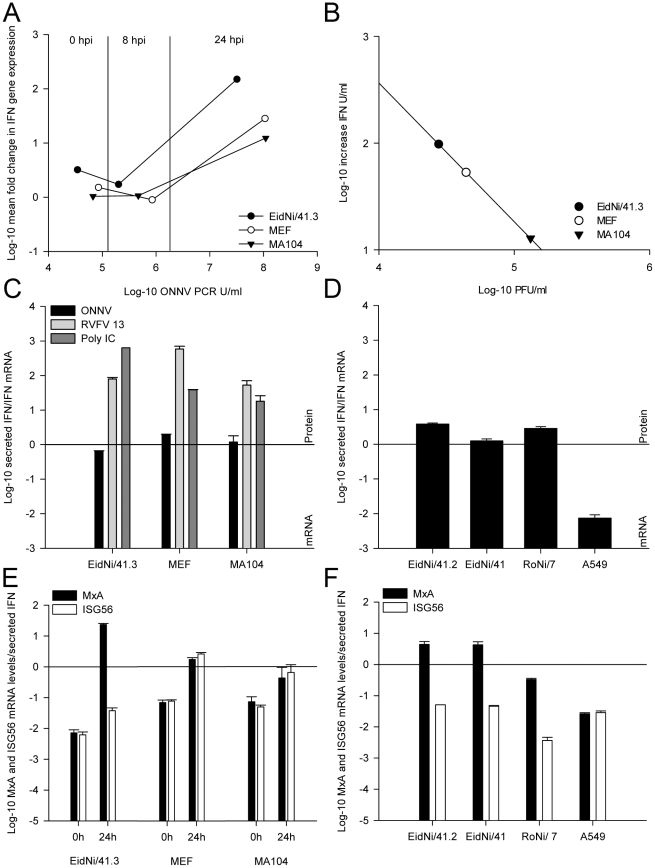
Figure 5. IFN-β mRNA induction but IFN protein decrease in all mammalian cells upon ONNV infection.
(A) IFN-β mRNA induction was measured by species-specific real-time RT-PCR at time points 0, 8 and 24 hpi and correlated to the amount of relative ONNV genome equivalents in PCR units per ml. ONNV replication led to an induction of IFN-β mRNA 24 hpi. (B) At 24 hpi the increase of secreted IFN was correlated to ONNV plaque forming units indicating that higher virus titres led to a decreased amount of IFN in the supernatants. (C) Comparison of secreted IFN protein to IFN-β mRNA (24 hpi) after ONNV, RVFV 13 infection and poly IC transfection. ONNV replication was related to IFN protein reduction. For absolute values refer to Figure S1. (D) Confirmation for IFN protein reduction by testing different EidNi bat cell cultures. EidNi/41.2 (subclone), EidNi/41 (mixed cell culture), RoNi/7 (mixed cell culture from R. aegyptiacus kidneys) and human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line (A549) showed the same phenotype. (E) Comparison of mRNA fold-induction of IFN stimulated genes (MxA and ISG56) to secreted IFN protein at time points 0 hpi and 24 hpi. Expression of ISGs was not affected by IFN protein downregulation indicating that there was no general transcriptional shutoff. (F) Confirmation by testing different cell clones and cell cultures 24 hpi indicating that MxA mRNA is upregulated in bat cell cultures upon ONNV infection.