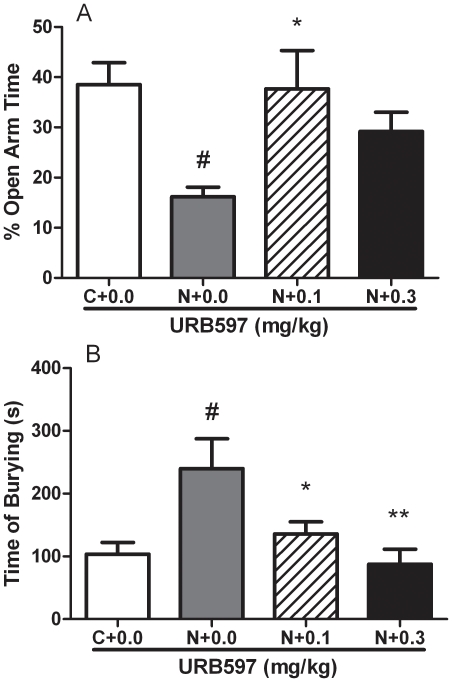
Figure 3. URB597 blocked nicotine withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior, as assessed in the elevated plus-maze and in the shock-probe defensive burying tests 34 hours after nicotine discontinuation.
(A) Animals previously exposed to nicotine (N+0.0) showed significant reduction in percent (%) open arm time compared to controls (C+0.0). URB597 returned % open arms time to control levels. Values represent the mean (±SEM) of N = 10–11 subjects per group. (B) Animals previously exposed to nicotine (N+0.0) showed significant increase in burying time (seconds) compared to controls (C+0.0). URB597 dose-dependently returned burying time to control levels. Values represent the mean (±SEM) of N = 7–8 subjects per group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared to nicotine exposed receiving vehicle; #p<0.05, difference from non-nicotine exposed controls.