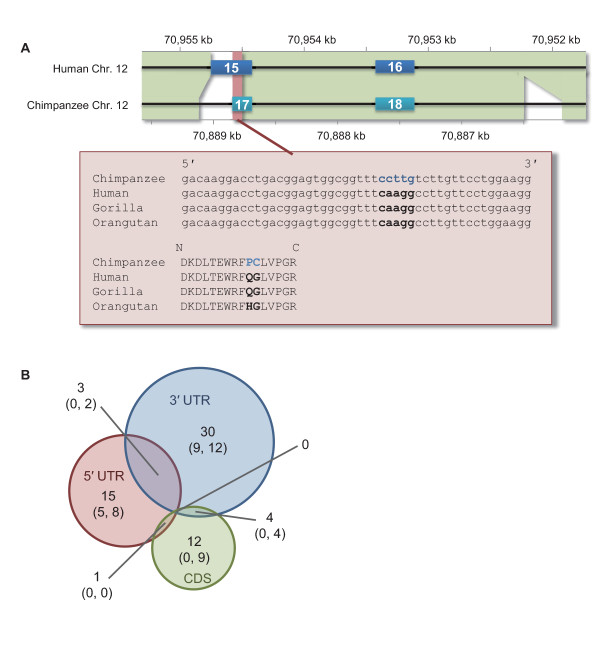
Figure 3.
Ultramicro inversions found within genes. (A) The multiple alignment around the ultramicro inversions specifically identified in the chimpanzee lineage in receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase beta genes (PTPRB) and the genomic structures of a part of PTPRB transcripts in the human (HIT000321866 from H-InvDB) and chimpanzee genomes (XM_509219 from Refseq). This inversion is included in one of the Fibronectin type III domains in a tandem array in PTPRB protein. Bold blue characters indicate the ultramicro inversion. Numbers within the boxes represent the exon numbers. The genomic regions with green and red backgrounds are subject to one-to-one alignment, and the red background corresponds to the multiple alignment. (B) Venn diagram of the ultramicro inversion frequencies in coding region sequences (CDS), 5' UTR, and 3' UTR. Numbers in parenthesis represent the ultramicro inversion frequencies that were inferred to have occurred specifically in the human and chimpanzee lineages, respectively. No ultramicro inversions in the genes showed the incomplete lineage sorting among human, chimpanzee, and gorilla.