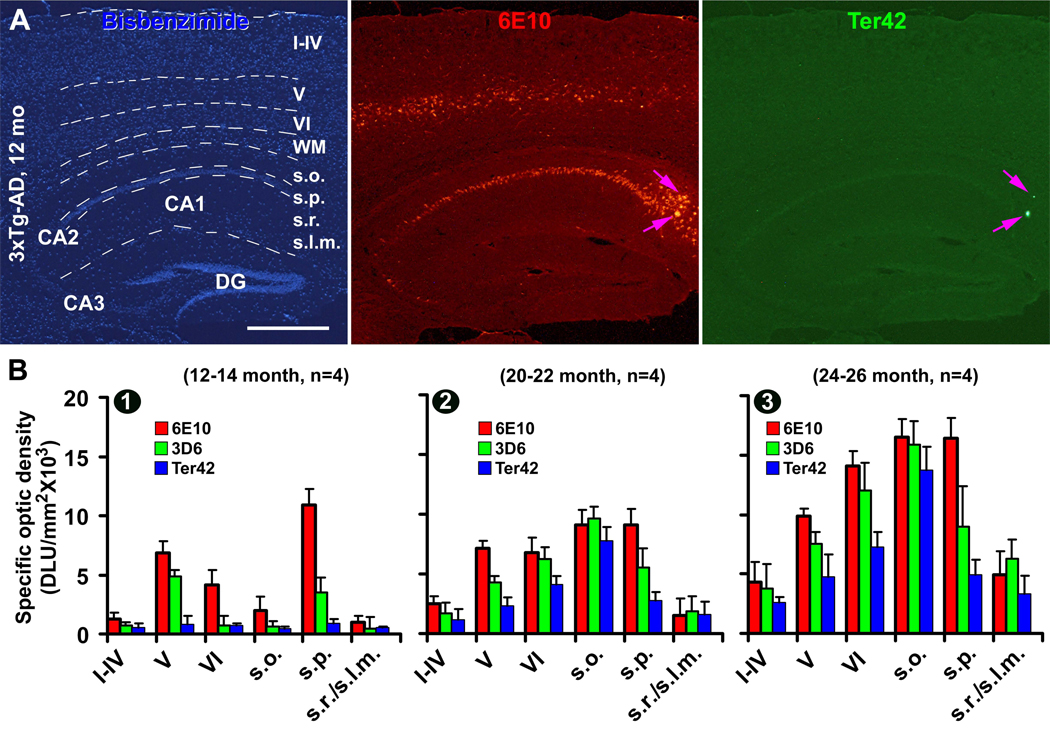
Fig. 6.
Densitometry of representative Aβ antibody (6E10, 3D6 and Ter42) immunolabeling in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in 3xTg-AD mice focusing on age-related laminar development of extracellular amyloid deposition. Panel (A) illustrates the methodology for concurrent lamina-based densitometry for two antibodies (raised in mouse and rabbit) using the OptiQuant imaging analysis software. A measuring template is created in the bisbenzimide-counterstained image, which is used to obtain optic densities of immunofluorescence over different cortical and hippocampal layers. In the 12–14 month-old group (B1), means of specific optic density of 6E10 and 3D6 immunoreactivities are high in cortical layers V and VI and hippocampal stratum pyramidale (s.p.), whereas the density of Ter42 reactivity is minimal across the cortex and hippocampus. A great increase of specific optic density occurs in the stratum oriens (s.o.) in the 20–22 month group for the 3 markers (B2). In the 24–26 month group, the deep cortex and stratum oriens show the highest density for all the 3 antibodies (B3). Abbreviations are as defined in Fig. 1.