Figure 4. Lin28B directly binds and sequesters pri-let-7.
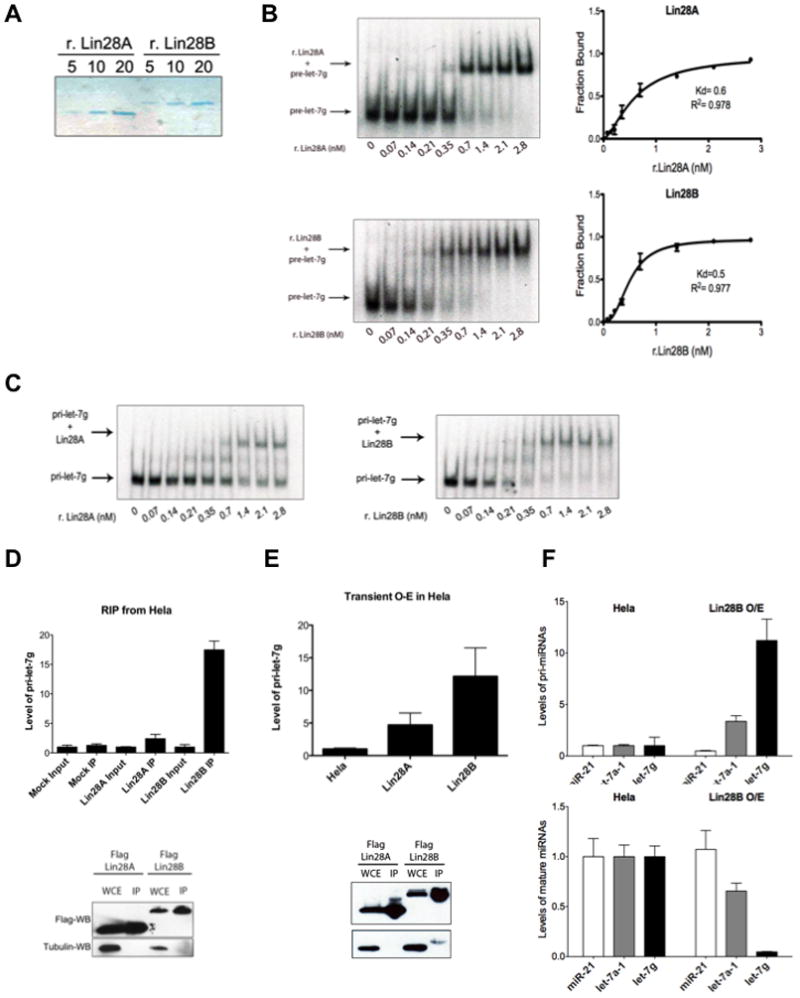
(A) Colloidal Blue staining of purified recombinant His-Lin28A and His-Lin28B proteins. (B) Binding of r.Lin28A and r.Lin28B to pre-let-7g was assessed by EMSA performed with 0.5 nM 5′-end labeled pre-let-7g RNA and the indicated concentration of recombinant protein. Band intensities were quantitated from three independent experiments and represented as the fraction of bound pre-let-7g RNA in the plots. Values are given as average ±S.E.M. (n=3). See also Figure S2. (C) EMSA performed indicated concentration of r.Lin28A and r.Lin28B with in vitro transcribed uniformly labeled pri-let-7g. (D) RNA-Immunoprecipitation (RIP) analysis of RNA associated with immunopurified Flag-Lin28A and Flag-Lin28B from Hela cells. RNA was extracted from IP material and analyzed by q.RT-PCR. Error bars ±S.E.M. (n=3). Lower panel indicates relative Lin28A and Lin28B expression levels by Flag-Western blot. (E) Accumulation of pri-let-7 by transient Lin28B expression in Hela cell detected by q.RT-PCR. Error bars ±S.E.M. (n=3). Lower panel indicates relative expression levels of Lin28A and Lin28B proteins detected by Flag-Western blot in transfected cells. (F) pri-let-7 accumulates (top panel) and mature let-7 levels decrease (bottom panel) in Hela cells stably overexpressing Lin28B. Error bars ±S.E.M. (n=3)
