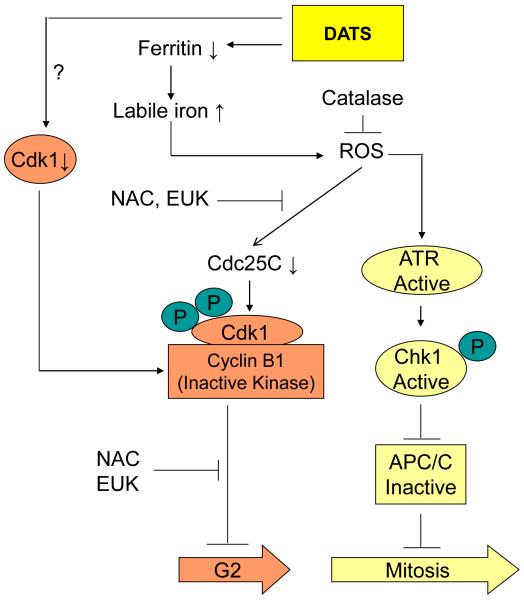
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms of DATS-induced cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells43-48. The DATS treatment causes degradation of ferritin to cause an increase in levels of labile iron leading to ROS generation. The DATS-induced ROS generation results in down-regulation of Cdc25C, which is attenuated in the presence of antioxidants such as N-acetylcysteine and superoxide dismutase and catalase mimetic EUK134. The DATS treatment down-regulates Cdk1 expression in prostate cancer cells, but the mechanism of this effect is not yet clear. Mitotic arrest resulting from DATS exposure, characterized by accumulation of cyclin B1 and securin, is caused by checkpoint kinase 1-dependent inactivation of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome.