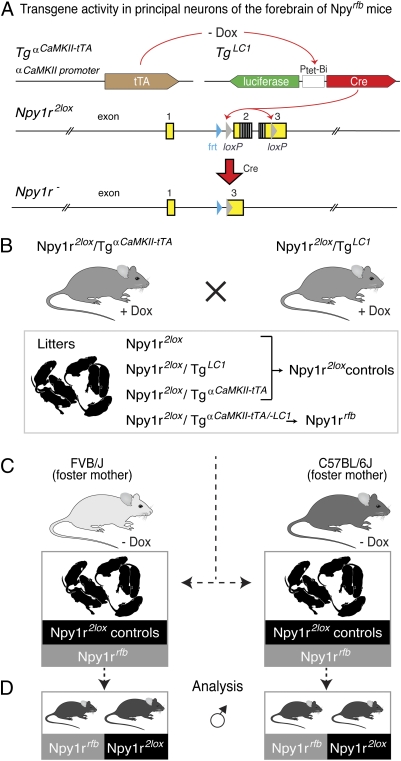
Fig. 1.
Generation of Npy1rrfb mutants and Npy1r2lox control cohorts used for the analysis. (A) Diagram depicting the interaction of the different genetic components: After Dox removal, the αCamKII promoter-driven tTA activates transcription of the transgene TgLC1, thereby inducing Cre expression in excitatory neurons of the forebrain. The Cre recombinase interacts with loxP sites in the gene-targeted Npy1r2lox alleles and removes the Npy1r2lox (SI Materials and Methods) coding region leading to the inactivation of the Npy1r gene (Npy1r−). Frt and loxP sites are in blue and gray triangles, respectively; exons in open boxes, coding regions in gray boxes; black boxes, transmembrane spanning codons. (B) By mating the compound transgenic mice Npy1r2lox/TgαCamKII-tTA and Npy1r2lox/TgLC1 under Dox treatment, pups with four different genotypes were generated and found in a Mendelian ratio. (C) At the day of birth [postnatal day (P)0], the litters were transferred to either C57BL/6J or FVB/J Dox naive foster mothers to induce the Cre-mediated Npy1r gene inactivation in the forebrain of Npy1r2lox/TgαCamKII-tTA/LC1 mice (named herein Npy1rrfb). Littermates comprising Npy1r2lox/TgαCamKII-tTA, Npy1r2lox/TgLC1, and Npy1r2lox genotypes were used as controls (named herein Npy1r2lox controls). (D) The comparative analysis of Npy1rrfb and Npy1r2lox controls was used to uncover the function of Y1R in the limbic system of mice that experienced differences in maternal care during the first three weeks of life, as indicated by increased body weight of adult Npy1r2lox mice fostered to FVB/J dams compared with other littermates.