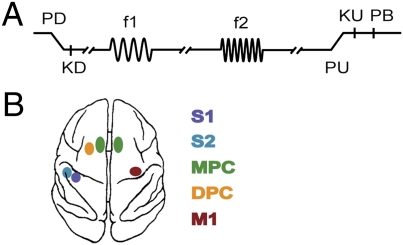
Fig. 1.
Somatosensory discrimination task. (A) Sequence of events during discrimination trials is shown. The mechanical probe is lowered, indenting the glabrous skin of one digit of the restrained hand (PD); the monkey places its free hand on an immovable key (KD); the probe oscillates vertically at the base frequency (f1); after a fixed delay (3 s), a second mechanical vibration is delivered at the comparison frequency (f2); and, after another fixed delay (3 s) between the end of f2 and probe up (PU), the monkey releases the key (KU) and presses either a lateral or medial push button (PB) to indicate whether the comparison frequency (f2) was higher or lower than the base (f1). (B) Overview of recording sites. During each recording session, up to seven electrodes were individually placed in each of the five cortical regions: primary somatosensory cortex (S1), secondary somatosensory cortex (S2), dorsal premotor cortex (DPC), medial premotor cortex (MPC), and primary motor cortex (M1). Both spikes and LFPs were obtained simultaneously through the same microelectrode.