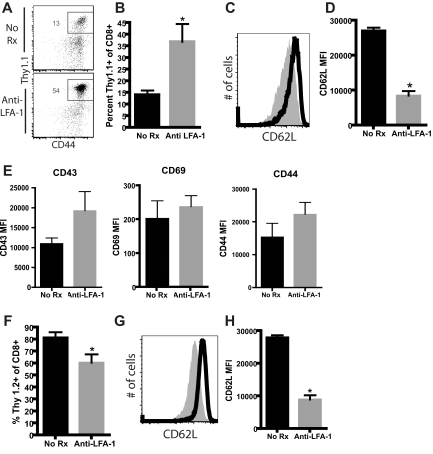
Figure 4.
Activated lymphocytes are preferentially sequestered in Ag-exposed, anti–LFA-1–treated LNs. mOVA graft–specific OT-I T cells were adoptively transferred into B6 recipients; 48 hours later, mice received an mOVA skin graft and were left untreated or were treated with anti–LFA-1. Draining LNs were harvested on day 10 after transplantation and donor-reactive Thy1.1+ T cells and non-donor-reactive endogenous Thy1.2+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A-B) LNs isolated from anti–LFA-1–treated animals demonstrated a greater percentage of Ag-specific, Thy 1.1+ CD8+ T cells compared with LNs isolated from untreated control animals (P = .018). (C-E) Down-regulation of CD62L expression on Thy1.1+ graft–specific T cells was observed after treatment with anti–LFA-1 compared with untreated controls (P < .0001), but there was no difference in the expression of CD43, CD69, and CD44 on these cells. (F) Analysis of endogenous, non-Ag-specific Thy1.2+ CD8+ T cells revealed a reduction in the frequency of cells compared with untreated controls (P = .023). (G-H) Thy1.2+ cells also exhibited decreased expression of CD62L expression (P < .0001) compared with untreated controls. Data shown are either representative (flow plots) or cumulative (bar graphs) from 2 independent experiments with a total of 8-9 mice per group.