Abstract
In axon-bearing neurons, action potentials conventionally initiate at the axon initial segment (AIS) and are important for neuron excitability and cell-to-cell communication. However in axonless neurons, spike origin has remained unclear. Here we report in the axonless, spiking AII amacrine cell of the mouse retina a dendritic process sharing organizational and functional similarities with the AIS. This process was revealed through viral-mediated expression of channelrhodopsin-2-GFP with the AIS-targeting motif of sodium channels (NavII-III). The AII processes showed clustering of voltage-gated Na+ channel 1.1 (Nav1.1) as well as AIS markers ankyrin-G and neurofascin. Furthermore, NavII-III targeting disrupted Nav1.1 clustering in the AII process, which drastically decreased Na+ current and abolished the ability of the AII amacrine cell to generate spiking. Our findings indicate that, despite lacking an axon, spiking in the axonless neuron can originate at a specialized AIS-like process.
Introduction
Sites of action potential generation have been implicated as important sources of neuronal plasticity and neuronal signaling optimization (Losonczy et al., 2008; Grubb and Burrone, 2010a; Kuba et al., 2010). Although it is known that action potentials typically initiate at the axon initial segment (AIS) in axon-bearing neurons (Coombs et al., 1957; Palmer and Stuart, 2006; Kole et al., 2008), the origin of action potentials in axonless neurons remains poorly understood.
The AII amacrine cell is an axonless interneuron in the mammalian retina known for its crucial role in mediating scotopic (nighttime) vision (Famiglietti and Kolb, 1975; Bloomfield and Dacheux, 2001) and recently also for its involvement in photopic (daytime) vision (Xin and Bloomfield, 1999; Manookin et al., 2008; Münch et al., 2009). The cell is conventionally depicted as a bistratified neuron with the following two distinct dendritic trees: the distal dendrites (arboreal dendrites) terminate in the retinal inner plexiform layer (IPL) ON-sublamina, and the proximal dendrites (lobular appendages) terminate in the OFF-sublamina. AII amacrine cells pass rod signals from rod bipolar cells received through the arboreal dendrites to the ON cone pathway at the arboreal dendrites, and to the OFF cone pathway at the lobular appendages (Bloomfield and Dacheux, 2001) (see Fig. 1a). Although it is commonly believed that AII amacrine cells primarily use graded potentials for information processing, accumulating evidence suggests that action potentials, or spikes, also play a role (Boos et al., 1993; Veruki and Hartveit, 2002a; Veruki and Hartveit, 2002b; Tamalu and Watanabe, 2007; Tian et al., 2010). Na+ channel-dependent spiking in the AII amacrine cell is well documented (Boos et al., 1993; Tamalu and Watanabe, 2007). A previous study suggested that Na+ channels are mainly localized in the soma and the proximal dendrites (Tamalu and Watanabe, 2007) (but see also Tian et al., 2010). The precise location and the nature of spike origin, however, have remained elusive.
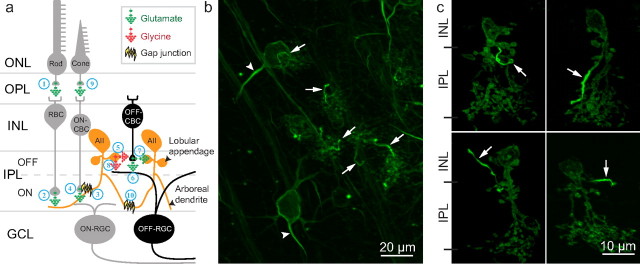
Figure 1.
AII amacrine cell circuits and ChR2-GFP-NavII-III expression in the retina. a, In scotopic vision, rods sense light and excite rod bipolar cells (RBCs) (1); RBCs synapse onto AII cell arboreal dendrites that excite ON-cone bipolar cells (CBCs) through gap junctions (2–3); ON-CBCs excite ON-RGCs (4); at the same time, AII cell lobular appendages inhibit OFF-CBC glutamate release onto OFF-RGCs and receive synaptic feedback from OFF-CBCs (Anderson et al., 2011) (5–7); lobular appendages also directly inhibit OFF-RGCs with glycine (8); therefore, excitation of AII cells leads to excitation of ON-pathways and inhibition of OFF-pathways; in photopic vision, cones sense light and excite ON-CBC that may use gap junctions in reverse to excite AII cells at the arboreal dendrites leading to inhibition of the OFF-pathway (9) (Manookin et al., 2008; Münch et al., 2009); and finally, AII cells are electrically coupled through arboreal dendrite gap junctions (10). ONL/OPL, Outer nuclear/plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; b, In retinal flat-mount, NavII-III expression was concentrated in RGC AIS (arrowheads) and smaller processes (arrows) suspected to belong to AII cells. Collapsed z-stack image: 20× objective; 1 μm z-sections. c, In retinal vertical section, each AII cell was observed with one NavII-III targeted process (arrows) of varying direction and conformation originating from the lobular appendages and terminating in both IPL ON- and OFF-sublaminae and in the INL. Collapsed z-stack image: 63× objective; 0.6 μm z-sections.
In this study, we took advantage of the cell's own protein trafficking machinery (Lai and Jan, 2006) and the high tropism of adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (AAV2/2) for the AII amacrine cell (Ivanova and Pan, 2009) to investigate the spike initiation site within this axonless neuron. Spike generation at the AIS requires voltage-gated Na+ (Nav) channel clustering (Kole et al., 2008). Nav1 subunits share a conserved amino acid motif (NavII-III) shown to be necessary and sufficient to target proteins to the AIS (Garrido et al., 2003; Lemaillet et al., 2003). By linking NavII-III to channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) for membrane anchoring, and GFP for visualization (also see Grubb and Burrone, 2010b), ChR2-GFP-NavII-III expression in the AII amacrine cell revealed an AIS-like compartment within its dendritic trees. This suggests that axonless neurons could possess similar compartmental organization as axon-bearing neurons for action potential generation.
Materials and Methods
DNA and viral vector construction.
AAV2/2 cassette carrying the ChR2-GFP fusion construct (Bi et al., 2006) was modified by inserting the 27 aa ankyrin binding domain from Nav1.6 (NavII-III: 5′-TVRVPIAVGESDFENLNTEDVSSESDP-3′) (Garrido et al., 2003) at the 3′ end of GFP. Virus vectors with CAG (a hybrid CMV early enhancer/chicken β-actin) promoter were packaged and affinity purified at the Gene Transfer Vector Core of the University of Iowa.
Animals and AAV2/2 vector injection.
All animal experiments and procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee at Wayne State University, and were in accord with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Adult C57BL/6J mice of either sex aged 1–2 months were used for virus injections. The procedures for virus injection were the same as previously described (Bi et al., 2006). Three groups of animals were injected. The motif-targeted group received injections of AAV2/2-ChR2-GFP-NavII-III virus at low and high concentrations of 5 × 1010 and 3–13 × 1012 genomic particles (GP)/ml for histology/immunohistochemistry and patch-clamp recordings, respectively. The injected-control group received injections of AAV2/2-ChR2-GFP virus at 4 × 1012 GP/ml. Animals were used for experiments at least 1 month after viral injection.
Histology/immunohistochemistry and data analysis.
Animals were killed by CO2 asphyxiation followed by decapitation and enucleation. Enucleated eyes were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in phosphate buffer (PB) at room temperature (RT) for 20 min. GFP expression was examined in flat-mounted retinas and vertical sections. For vertical sections, fixed retinas were cryoprotected in a sucrose gradient and cryosectioned at 20 μm thickness. Slides with cryosections were washed 3 × 20 min in PB followed by a 40 min incubation in blocking solution that contained 5% Chemiblocker (Millipore Bioscience Research Reagents), 0.5% Triton X-100, and 0.05% sodium azide. For immunostaining, the following primary antibodies were diluted in blocking solution and applied to sections for overnight RT incubation: mouse anti-ankG (1:20,000; Neuromab), rabbit anti-pan-NF (1:2000; Abcam), mouse anti-Nav1.1 (1:4000; Neuromab), rabbit anti-SPo (1:60,000; Synaptic Systems), and mouse anti-GlyRα1 (1:4000; Synaptic Systems). The next day, slides were washed 3 × 20 min in PB and secondary antibodies diluted in blocking solution were applied for a 1 h RT incubation in the dark. Slides were then washed 3 × 20 min in PB and mounted in Vectashield (Vector Laboratories) for fluorescence microscopy. All z-stack images were acquired using a Zeiss Axioplan 2 microscope with Apotome (Carl Zeiss) with the AxioVision software. Images were processed using Adobe Photoshop CS5.
The analysis of the relationship between ChR2-GFP-NavII-III expression and Nav1.1 immunostaining was performed from collapsed images of retinal vertical sections of retinas injected with low virus concentration. Two mean fluorescence intensities (FIs) were measured in each AII process using ImageJ (obtained from NIH) by applying a 5-pixel-wide line tracing the AII process: one for GFP FI and the other for Nav1.1 immunostaining FI. Each collapsed image analyzed contained more than three AII processes, with at least one showing GFP labeling without Nav1.1 immunostaining, at least one showing Nav1.1 immunostaining without GFP labeling, and at least one that is both labeled by GFP and immunostained for Nav1.1. The measured FIs for GFP and Na1.1 after background subtraction were normalized to the highest GFP FI and Na1.1 FI, respectively. The normalized Nav1.1-FI was plotted against the GFP-FI, and the relationship was analyzed using linear regression.
Electrophysiological recordings.
Retinal slices were prepared as previously described (Ivanova and Pan, 2009). Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in control were performed in oxygenized HANKS solution (in mm), as follows: NaCl 136.8; KCl 5.4; KH2PO4 0.4; NaH2PO4 0.3; CaCl2 1.3; MgCl2 0.5; MgSO4 0.5; HEPES 5.0; d-glucose 22.0; phenol red 0.03; pH 7.2. The recordings of current injection-evoked spike activity were performed in HANKS with CNQX (15 μm), strychnine (1 μm), and picrotoxinin (50 μm). The recordings of voltage-gated Na+ current were performed in HANKS with CdCl2 (100 μm), tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA-Cl; 10 mm), CNQX (15 μm), strychnine (1 μm), and picrotoxinin (50 μm). The intracellular solution was as follows (in mm): Cs-acetate 130.0; TEA-Cl 10; EGTA 0.1; MgCl2 4.0; HEPES 10; NaATP 2.0; NaGTP 0.5; Alexa Fluor 568 hydrozide sodium salt (Invitrogen) 0.1; pH 7.4. Tetrodotoxin (1 μm) was applied to block Na+ current. All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Liquid junction potential (3 mV) was corrected. The resistance of the electrode was ∼8 MΩ. Pipette and cell capacitances were canceled. Data were analyzed off-line using the ORIGIN (Microcal Software) program.
Results
Viral-mediated NavII-III-targeted expression in the retina
In vivo expression of ChR2-GFP-NavII-III in the mouse retina was achieved through AAV2/2-mediated gene delivery by intravitreal injection (Bi et al., 2006). As expected, ChR2-GFP-NavII-III expression in the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) was concentrated in the AIS (Fig. 1b, arrowheads). In addition, GFP fluorescence was brightly concentrated in smaller processes throughout the IPL (Fig. 1b, arrows). We suspected these processes belonged to AII amacrine cells due to the high tropism of AAV2/2 for AII cells (Ivanova and Pan, 2009). Indeed, in vertical section each process (hereafter referred to as the AII process) was found to originate from one AII cell at the lobular appendages. AII processes were varied in orientation and conformation, and terminated in both ON- and OFF-sublaminae of the IPL and occasionally in the inner nuclear layer (INL) (Fig. 1c).
Immunohistochemical staining of AIS-associated proteins in AII processes
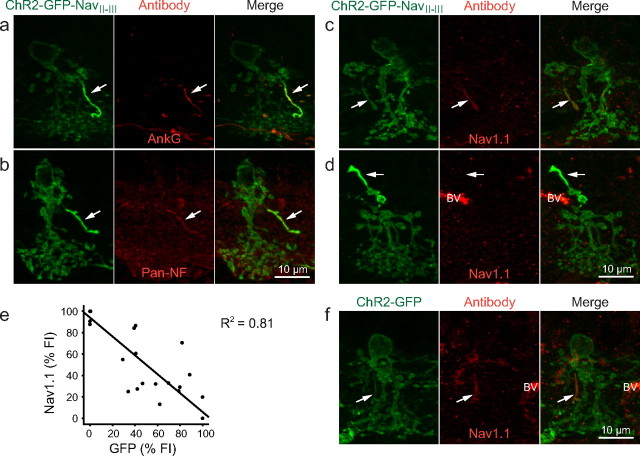
Because NavII-III is an AIS-targeting motif, we first examined the AII processes with immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for proteins typically enriched at the AIS. NavII-III contains an ankyrin binding domain, which binds the cytoskeletal scaffold protein ankyrin-G (ankG) at the AIS (Garrido et al., 2003; Lemaillet et al., 2003). In vertical sections, ankG immunostaining colocalized with AII processes (Fig. 2a). Similarly, pan-neurofascin (pan-NF) immunostaining against an axonal cell adhesion molecule that functions in the organization of the AIS (Sherman et al., 2005; Hedstrom et al., 2007), also colocalized with AII processes (Fig. 2b).
Figure 2.
IHC characterization of AIS markers in NavII-III-targeted AII processes. a, b, In AII cells expressing ChR2-GFP-NavII-III, AII processes colocalized with the AIS markers ankG (a) and pan-NF (b). c, In weakly targeted AII processes, Nav1.1 colocalization was observed. d, In strongly targeted AII processes, Nav1.1 colocalization was not seen. BV, Blood vessel. e, Scatter plot with linear regression line summarizing the inverse relationship between the normalized FIs of ChR2-GFP-NavII-III expression and Nav1.1 immunostaining in ChR2-GFP-NavII-III targeted AII processes. f, Nav1.1 immunostaining also colocalized at an elongated process in nontargeted ChR2-GFP-expressing AII cells. All images are collapsed z-stack image: 63× objective; 0.6 μm z-sections.
Since voltage-gated sodium channels cluster at the AIS and in situ hybridization studies have shown AII amacrine cells to express the Nav1.1 subunit (Kaneko and Watanabe, 2007), we anticipated every AII process to immunostain positively for Nav1.1. However, Nav1.1 immunostaining produced a spectrum of results in retinas infected with a low virus concentration (see Materials and Methods). Certain AII processes stained positively for Nav1.1 (Fig. 2c), while others appeared virtually unstained (Fig. 2d). The Nav1.1 staining appeared to be inversely related to the FI of GFP. To quantitatively examine this effect, we measured the FIs of Nav1.1 staining and GFP from each individual AII process (n = 31). The plot of the normalized Nav1.1-FI against the normalized GFP-FI indeed display an inverse relationship (β = −0.90, F(1,29) = 121.3, R2 = 0.81, p < 0.001) (Fig. 2e). The results suggest that the targeted expression of ChR2-GFP-NavII-III is in competition with endogenous Nav1.1 for ankG binding at the AII processes.
Since it might be possible that the expression of ChR2-GFP-NavII-III also competes with Nav1.1 in other processes of AII cells, to further assess the distribution of Nav1.1 we examined the Nav1.1 staining in GFP-labeled AII cells from eyes injected with virus carrying ChR2-GFP (without the NavII-III motif). Nav1.1 immunostaining was only observed in a single elongated process (presumably the AII process) in AII cells, while staining in other processes of AII cells was indistinguishable from the background (Fig. 2f), similar to the background staining in AII cells expressing ChR2-GFP-NavII-III (Fig. 2c,d). These results suggest that Nav1.1 channels in the AII cells are predominantly, if not exclusively, localized at the AII process. The competition between ChR2-GFP-NavII-III and Nav1.1 is therefore likely to be limited to the AII process.
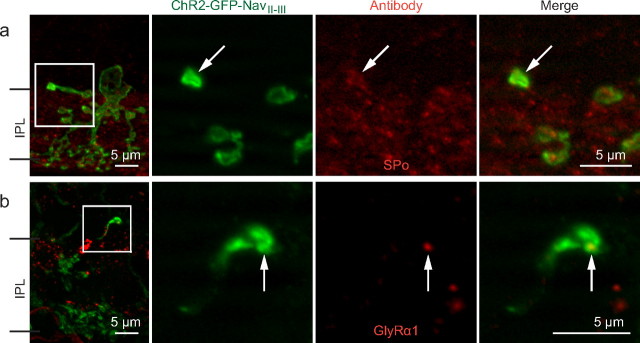
IHC of lobular appendage-associated elements in AII processes
AII processes have AIS features, yet they still resemble lobular appendages, particularly at the distal ends where lobules are often formed. To explore this relationship, we immunostained for the major synaptic vesicle protein found in lobular appendages, synaptoporin (SPo) (Brandstätter et al., 1996). In vertical sections, 97% (n = 58) of AII processes examined colocalized with SPo immunostaining (Fig. 3a). To investigate whether AII processes potentially had a postsynaptic partner, we immunostained vertical sections with antibodies against the glycine receptor α1 subunit (GlyRα1) postsynaptic to lobular appendages (Sassoè-Pognetto et al., 1994; Grünert and Wässle, 1996). When NavII-III expressing AII processes were examined, 84% (n = 45) appeared to colocalize with GlyRα1 puncta (Fig. 3b) (GlyRα1). These results suggest that AII processes likely contain the sites of presynaptic glycine release.
Figure 3.
IHC characterization of lobular appendage features in AII processes. a, b, The first panels are z-stack projections (20× objective; 1 μm z-sections), and three subsequent panels are single-plane magnifications (63× objective, 0.6 μm z-sections) of the corresponding boxed areas showing an AII process terminal colocalizing with SPo immunostaining (a) and an AII process colocalizing with a GlyRα1 punctum (b).
Patch-clamp characterization of NavII-III-targeting on AII cell spiking
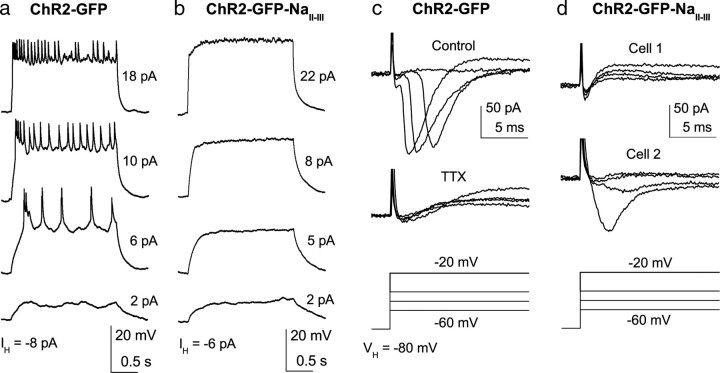
Because the expression of ChR2-GFP-NavII-III disrupts endogenous Nav1.1 clustering in AII processes, we examined this effect on the spiking ability of AII amacrine cells by performing whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in retinal slices. We first examined action potentials evoked by current injection in current-clamp with the suppression of all synaptic inputs. As a control, we recorded GFP-labeled AII cells from eyes injected with virus carrying ChR2-GFP without the NavII-III motif. Consistent with previous reports (Boos et al., 1993; Tamalu and Watanabe, 2007), spike-like potentials were evoked in the majority of recorded AII cells (11 of 13) (Fig. 4a). In contrast to the control, no spike-like potential was observed with current injection in any of the recorded AII cells in the NavII-III targeted group (n = 7) (Fig. 4b). For every cell recorded in both groups, the functional expression of ChR2 was confirmed by the ChR2-mediated light responses (data not shown). Thus, AII amacrine cells with NavII-III motif-targeted expression of ChR2-GFP lost their spike firing ability.
Figure 4.
Patch-clamp recordings of Na+ channel-mediated action potentials and Na+ current in AII cells. a, b, Depolarizing current injections from ∼−80 mV elicited spikes in an AII cell in the control group (a), but not in the NavII-III targeted group (b). Injection currents relative to the holding current are shown. c, d, Na+ currents activated by membrane depolarization of AII cells from the holding potential of −80 mV. c, Top, A representative recording from a cell in the control group. Bottom, The current in the same cell was blocked by 1 μm TTX. d, Recordings from the NavII-III targeted group of a cell with no Na+ current (cell 1, top) and a cell with the largest Na+ current (cell 2, bottom).
We next compared the voltage-gated Na+ current between control and NavII-III targeted groups. The recordings were made under the condition that other voltage-gated currents and neurotransmitter-activated receptors were blocked to isolate Na+ currents. Na+ currents were observed in the majority of recorded AII cells in the control group (5 of 7) (Fig. 4c) but were barely detected in the majority of the NavII-III-targeted group (Fig. 4d, top). Only in a few cells (3 of 13) were small or moderate Na+ currents observed (Fig. 4d, bottom). The current observed in these few cells is likely due to the variable disruption of Nav1.1 at the AII process. The average (±SEM) peak current for the control group (84.3 ± 24.7; n = 7) was significantly different from that of the NavII-III targeted group (6.4 ± 4.3 SEM; n = 13; p < 0.001, two-tailed t test). Together, these results indicate that targeted ChR2-GFP-NavII-III expression largely abolished Na+ currents along with the spiking ability of AII amacrine cells.
Discussion
In this study, we revealed the clustering of Na+ channels at an AIS-like process in the AII amacrine cell. We also demonstrated that the clustering of Na+ channels in the process is essential for spike generation in this axonless neuron. These AIS-like processes are likely the morphologically distinct processes immunolabeled by Nav1.1, ankyrin-G and neurofascin reported in the rat retina (Van Wart et al., 2005), but the previous study was unable to link these processes to their cells of origin. Our results thus show an advantage of motif-targeted fluorescent protein expression in identifying this elusive compartment in the AII amacrine cell.
In several aspects, the AII processes resemble the lobular appendages because they originate at the primary dendrite and terminate with lobular appearance where lobular appendage-associated elements are expressed. However, unlike the classic lobular appendages, the processes were found to terminate throughout the IPL and even in the INL. In addition, the AII processes are generally longer and more slender than the typical lobular appendages. Therefore, the AII process appears to be morphologically distinct from conventional lobular appendages.
What might be the functional role of Na+ channel clustering at this unconventional AIS-like process in the AII amacrine cell? First, as in the case of AIS in the axon-bearing neurons, the AIS-like process could facilitate spiking by lowering the threshold of spike generation in AII cells (Kole et al., 2008). Second, since the terminal of AII processes appear to contain functional synapses, the clustering of Na+ channels would be expected to elicit strong neurotransmitter release from this particular site and, thus, provide fast inhibitory signaling, possibly to both ON and OFF downstream pathways. Furthermore, the AII process is likely to be electrotonically closer to the lobular appendages than the arboreal dendrites. Therefore, the AIS-like process may serve to differentially amplify and accelerate rod signals (Boos et al., 1993; Smith and Vardi, 1995) to downstream ON and OFF pathways. However, a recent study reported that although AII cell action potentials accelerated the light response of RGCs, blocking voltage-gated Na+ channels did not differentially affect ON and OFF responses or attenuate the response amplitudes of RGCs in scotopic vision (Tian et al., 2010). The latter is surprising because action potentials in AII cells have been shown to be able to transmit through electrical synapses between AII cells and to downstream cone bipolar cells (Veruki and Hartveit, 2002a,b). Since the spiking ability of AII cells is dependent on their membrane potentials and possibly modulated by other factors (Boos et al., 1993; Tian et al., 2010), the functional role of voltage-gated Na+ channels and the clustering of the Na+ channels of AII cells in rod signal processing needs to be further investigated. Finally, with extensive synaptic connectivity with at least 12 different classes of retinal neurons (Anderson et al., 2011) and the recent findings of new roles of AII cells in photopic vision (Manookin et al., 2008; Münch et al., 2009), it also remains to be studied whether AII cell action potentials generated at this AIS-like process could play a role in other information pathways.
Amacrine cells are the most morphologically and functionally diverse cell class in the retina (Masland, 1988). Action potentials mediated by voltage-gated Na+ channels in amacrine cells have also been reported to contribute to the receptive field size and directional selectivity of RGCs (Bloomfield, 1996; Oesch and Taylor, 2010). Dendritic spiking was proposed to play a role in the information processing of amacrine cells by computer modeling (Royer and Miller, 2007). The discovery of the AIS-like process in AII cells may offer new insights into the localization and function of voltage-gated Na+ channels in other spiking amacrine cells.
It remains to be seen whether the presence of AIS-like processes in axonless neurons could be a general feature in the CNS. Supporting such possibility, patch-like segments with AIS-characteristics have been reported in the dendritic processes of olfactory bulb granule cells (Kosaka et al., 2008), a population of axonless spiking interneurons that play a role in odor discrimination (Abraham et al., 2010). The same methods could be used to visualize possible AIS-like processes and assess their functional roles in axonless neurons in other regions of the nervous system. The approach of motif targeting could be a valuable tool for studying the structure and function of the CNS.
Footnotes
This work was supported by NIH Grant EY17130, the Wayne State University (WSU) MD/PhD program (C.W.), and NIH Core Grant EY04068 to the Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology at WSU. We thank Drs. R. Andrade and Dennis Goebel for comments on the manuscript.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Abraham NM, Egger V, Shimshek DR, Renden R, Fukunaga I, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH, Klugmann M, Margrie TW, Schaefer AT, Kuner T. Synaptic inhibition in the olfactory bulb accelerates odor discrimination in mice. Neuron. 2010;65:399–411. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson JR, Jones BW, Watt CB, Shaw MV, Yang J-H, Demill D, Lauritzen JS, Lin YH, Rapp KD, Mastronarde D, Koshevoy P, Grimm B, Tasdizen T, Whitaker R, Marc RE. Exploring the retinal connectome. Mol Vis. 2011;17:355–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi A, Cui J, Ma YP, Olshevskaya E, Pu M, Dizhoor AM, Pan ZH. Ectopic expression of a microbial-type rhodopsin restores visual responses in mice with photoreceptor degeneration. Neuron. 2006;50:23–33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.02.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield SA. Effect of spike blockade on the receptive-field size of amacrine and ganglion cells in the rabbit retina. J Neurophysiol. 1996;75:1878–1893. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.75.5.1878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield SA, Dacheux RF. Rod vision: pathways and processing in the mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001;20:351–384. doi: 10.1016/s1350-9462(00)00031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos R, Schneider H, Wässle H. Voltage-and transmitter-gated currents of all-amacrine cells in a slice preparation of the rat retina. J Neurosci. 1993;13:2874–2888. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-02874.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandstätter JH, Löhrke S, Morgans CW, Wässle H. Distributions of two homologous synaptic vesicle proteins, synaptoporin and synaptophysin, in the mammalian retina. J Comp Neurol. 1996;370:1–10. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960617)370:1<1::AID-CNE1>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs JS, Curtis DR, Eccles JC. The generation of impulses in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957;139:232–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famiglietti EV, Jr, Kolb H. A bistratified amacrine cell and synaptic cirucitry in the inner plexiform layer of the retina. Brain Res. 1975;84:293–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90983-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrido JJ, Giraud P, Carlier E, Fernandes F, Moussif A, Fache MP, Debanne D, Dargent B. A targeting motif involved in sodium channel clustering at the axonal initial segment. Science. 2003;300:2091–2094. doi: 10.1126/science.1085167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb MS, Burrone J. Activity-dependent relocation of the axon initial segment fine-tunes neuronal excitability. Nature. 2010a;465:1070–1074. doi: 10.1038/nature09160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb MS, Burrone J. Channelrhodopsin-2 localised to the axon initial segment. PLoS One. 2010b;5:e13761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünert U, Wässle H. Glycine receptors in the rod pathway of the macaque monkey retina. Vis Neurosci. 1996;13:101–115. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800007161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom KL, Xu X, Ogawa Y, Frischknecht R, Seidenbecher CI, Shrager P, Rasband MN. Neurofascin assembles a specialized extracellular matrix at the axon initial segment. J Cell Biol. 2007;178:875–886. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200705119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova E, Pan ZH. Evaluation of the adeno-associated virus mediated long-term expression of channelrhodopsin-2 in the mouse retina. Mol Vis. 2009;15:1680–1689. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y, Watanabe S. Expression of Nav1.1 in rat retinal AII amacrine cells. Neurosci lett. 2007;424:83–88. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole MH, Ilschner SU, Kampa BM, Williams SR, Ruben PC, Stuart GJ. Action potential generation requires a high sodium channel density in the axon initial segment. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:178–186. doi: 10.1038/nn2040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T, Komada M, Kosaka K. Sodium channel cluster, βIV-spectrin and ankyrinG positive “hot spots” on dendritic segments of parvalbumin-containing neurons and some other neurons in the mouse and rat main olfactory bulbs. Neurosci Res. 2008;62:176–186. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2008.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba H, Oichi Y, Ohmori H. Presynaptic activity regulates Na+ channel distribution at the axon initial segment. Nature. 2010;465:1075–1078. doi: 10.1038/nature09087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai HC, Jan LY. The distribution and targeting of neuronal voltage-gated ion channels. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:548–562. doi: 10.1038/nrn1938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaillet G, Walker B, Lambert S. Identification of a conserved ankyrin-binding motif in the family of sodium channel alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:27333–27339. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303327200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losonczy A, Makara JK, Magee JC. Compartmentalized dendritic plasticity and input feature storage in neurons. Nature. 2008;452:436–441. doi: 10.1038/nature06725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manookin MB, Beaudoin DL, Ernst ZR, Flagel LJ, Demb JB. Disinhibition combines with excitation to extend the operating range of the OFF visual pathway in daylight. J Neurosci. 2008;28:4136–4150. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4274-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masland RH. Amacrine cells. Trends Neurosci. 1988;11:405–410. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münch TA, da Silveira RA, Siegert S, Viney TJ, Awatramani GB, Roska B. Approach sensitivity in the retina processed by a multifunctional neural circuit. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:1308–1316. doi: 10.1038/nn.2389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch NW, Taylor WR. Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels contribute to directional responses in starburst amacrine cells. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer LM, Stuart GJ. Site of action potential initiation in layer 5 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 2006;26:1854–1863. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4812-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer AS, Miller RF. Dendritic impulse collisions and shifting sites of action potential initiation contract and extend the receptive field of an amacrine cell. Vis Neurosci. 2007;24:619–634. doi: 10.1017/S0952523807070617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoè-Pognetto M, Wässle H, Grünert U. Glycinergic synapses in the rod pathway of the rat retina: cone bipolar cells express the α1 subunit of the glycine receptor. J Neurosci. 1994;14:5131–5146. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-05131.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman DL, Tait S, Melrose S, Johnson R, Zonta B, Court FA, Macklin WB, Meek S, Smith AJ, Cottrell DF, Brophy PJ. Neurofascins are required to establish axonal domains for saltatory conduction. Neuron. 2005;48:737–742. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith RG, Vardi N. Simulation of the AII amacrine cell of mammalian retina: functional consequences of electrical coupling and regenerative membrane properties. Vis Neurosci. 1995;12:851–860. doi: 10.1017/s095252380000941x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamalu F, Watanabe S. Glutamatergic input is coded by spike frequency at the soma and proximal dendrite of AII amacrine cells in the mouse retina. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25:3243–3252. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M, Jarsky T, Murphy GJ, Rieke F, Singer JH. Voltage-gated Na channels in AII amacrine cells accelerate scotopic light responses mediated by the rod bipolar cell pathway. J Neurosci. 2010;30:4650–4659. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4212-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wart A, Boiko T, Trimmer JS, Matthews G. Novel clustering of sodium channel Na(v)1.1 with ankyrin-G and neurofascin at discrete sites in the inner plexiform layer of the retina. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005;28:661–673. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2004.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veruki ML, Hartveit E. AII (Rod) amacrine cells form a network of electrically coupled interneurons in the mammalian retina. Neuron. 2002a;33:935–946. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00609-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veruki ML, Hartveit E. Electrical synapses mediate signal transmission in the rod pathway of the mammalian retina. J Neurosci. 2002b;22:10558–10566. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10558.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin D, Bloomfield SA. Comparison of the responses of AII amacrine cells in the dark- and light-adapted rabbit retina. Vis Neurosci. 1999;16:653–665. doi: 10.1017/s0952523899164058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]