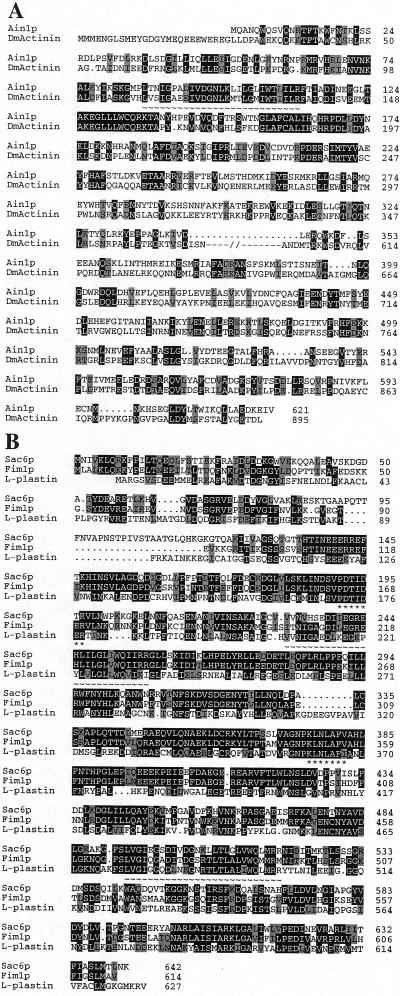
Figure 2.
Sequences of S. pombe Ain1p and Fim1p. (A) Alignment of Ain1p (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number Z97208) and Drosophila muscle α-actinin (DmActinin; accession number X51753). Proteins were aligned using the GCG GAP program with some modifications according to the results of a BLAST analysis (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/). Identical and similar (V/I/L, D/E, K/R, N/Q, S/T) amino acids are shaded in black and gray, respectively. Dots indicate gaps introduced to optimize the alignment; underscoring by ∼ indicates the presumed actin-binding motif; and –//– indicates amino acids 370 to 599 of DmActinin, omitted here to optimize alignment of the NH2- and COOH-terminal regions of the proteins (see text). (B) Alignment of Fim1p (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number AF053722), S. cerevisiae Sac6p (SWISS-PROT accession number P32599), and the human fimbrin L-plastin (SWISS-PROT accession number P13796). Proteins were aligned using the GCG PileUp program. Amino acids identical or similar (see above) to those in Fim1p are shaded in black and gray, respectively. Two putative actin-binding motifs are underscored with ∼. The amino acids of Sac6p and L-plastin underscored with * were used to design the degenerate PCR primers that allowed the cloning of fim1 (see MATERIALS AND METHODS).