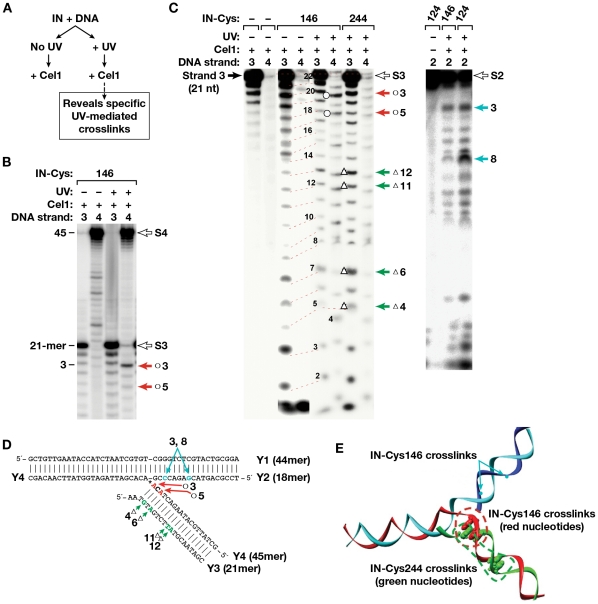
Figure 7. Cel 1-based localization of the crosslinking sites on the Y-mer DNA.
(A) The method for detecting specific UV-mediated crosslinks in Ymer DNA is outlined. (B) Cel 1 cleavage of the photocrosslinked complex of IN I146C. Products from Y-mer DNAs labeled at the 5′-end of strand 3 or 4 (marked above each lane) are shown. The filled arrows point to prominent Cel 1 products, indicative of a bulky adduct at the conserved viral CA dinucleotide in strand 4. Open arrows mark the position of non-cleaved substrate strands. (C) Cel 1 cleavage of various photocrosslinked complexes of Cys-modified derivatives of IN with Y-mer DNA labeled at strands 2, 3, or 4. Numbers above the gels indicate which DNA strand in the Y-mer was labeled. Open arrows mark the position of non-cleaved substrate strands. Numbers to the left of the gel indicate length in nucleotides, and arrows to the right mark the positions of adducts of IN with DNA. In both B and C, products were separated by denaturing gel electrophoresis and then visualized with a PhosphorImager. (D) Y-mer DNA sequence with positions of preferred crosslinking detected by Cel1 indicated for each IN derivative by red (I146C), green (R244C) and teal (S124C) arrows; (E) 3-D model of the Y-mer DNA with positions of preferred crosslinking detected by Cel1 indicated for each IN derivative by green (C244), red (C146) and teal (C124) dots.