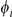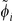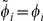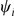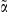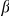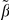|
μ
|
Population death rate |
1/50 years−1
|
Uninfected hosts have an average life expectancy of 50 years. This estimate is based upon a population in Southern Africa [36]. |
| B |
Population birth rate |
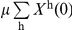
|
The population size is constant in the absence of infection. |
|
γ
|
Proportion of newborns who receive the vaccine at birth. |
0 for the first 50 years of the epidemic and 1 beyond year 50. |
No hosts receive the vaccine between years 0 and 50. Beyond year 50 all newborns receive the vaccine. Note that in addition we have assumed that all other hosts receive the vaccine at year 50. |
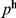
|
Proportion of hosts in the population with host type h
|
In Figure 7 different proportions are compared: 0.1k0.9n-k, 0.3k0.7n-k and 0.5k0.5n-k, where 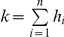 is the number of epitopes for which the host is HLA matched. In the remaining figures the proportion is 0.2k0.8n-k is the number of epitopes for which the host is HLA matched. In the remaining figures the proportion is 0.2k0.8n-k
|
Recognition of each epitope is assumed to be independent. In Figure 7 different percentages of the population recognising each epitope are considered: 10%, 30% and 50%. In the remaining figures 20% of the population recognise each epitope. |
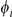
|
Rate of escape at epitope i in unvaccinated HLA matched hosts. |
In Figure 3 different escape rates (the same rate at each epitope) are compared: 1/3 years−1, 1/30 years−1 and 0 years−1. In Figure 5 rates ranging from 0 years−1 to 1/1000 years−1 are considered. In the remaining figures the rate at each epitope is 1/8 years−1
[22]. |
The reciprocal of the rate of escape is equal to the average time between infection and escape. |
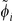
|
Rate of escape at epitope i in vaccinated HLA matched hosts. |
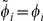
|
At each epitope escape occurs at the same rate in vaccinated and unvaccinated hosts. |
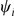
|
Rate of reversion at epitope i in HLA mismatched hosts. |
In Figure 4 different reversion rates (the same at each epitope) are compared: 1/3 years−1, 1/30 years−1 and 0 years−1. In Figure 5 rates ranging from 0 years−1 to 1/1000 years−1 are considered. In the remaining figures the rate at each epitope is 1/36 years−1
[22]. |
The reciprocal of the rate of reversion is equal to the average time between infection and reversion. |

|
Disease-related death rate of unvaccinated or unsuccessfully vaccinated hosts |
(1/10-µ) years−1
|
The average life expectancy in the absence of vaccine-induced protection (1/(µ+α)) is 10 years [37]. This estimate assumes that infected unvaccinated hosts do not receive treatment. |
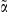
|
Disease-related death rate of successfully vaccinated hosts. |
0 years−1
|
Successfully vaccinated hosts have the same life expectancy as uninfected hosts. |
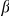
|
Transmission rate per partnership with an unvaccinated or unsuccessfully vaccinated host |
0.2/c |
In an unvaccinated population this yields a basic reproduction number of 2 [33]. |
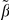
|
Transmission rate per partnership with a successfully vaccinated hosts. |
In Figure 2 different values are considered: 0.008/c and 0.1/c. In the remaining figures: 0.008/c |
In Figure 2 successfully vaccinated hosts are 25 times or 2 times less infectious compared to unvaccinated or unsuccessfully vaccinated hosts. In the remaining figures they are 25 times less infectious. |
|
c
|
Rate of partner exchange |
See above |
See above. |
|
r
|
Fraction of vaccinated hosts resistant to infection |
0 |
No hosts are resistant to infection |
|
n
|
Number of epitopes in the vaccine |
In Figure 6 different number of epitopes are considered: 1, 3 and 5. In the remaining simulations there are 5 epitopes. |
This is the number of epitopes that the vaccine is capable of inducing CTL responses to. |
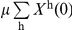
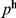
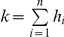 is the number of epitopes for which the host is HLA matched. In the remaining figures the proportion is 0.2k0.8n-k
is the number of epitopes for which the host is HLA matched. In the remaining figures the proportion is 0.2k0.8n-k