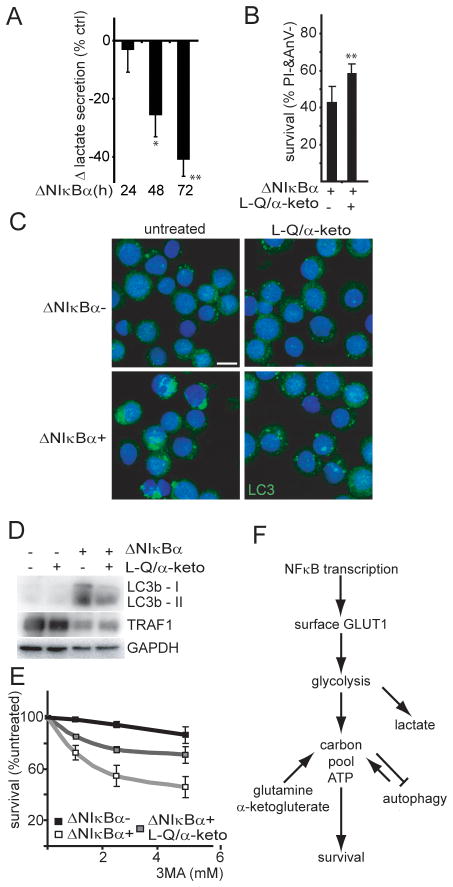
Figure 5. NFκB-mediated transcription links carbon availability to cell survival in a model of NFκB dependent lymphoma.
(A) Rate of lactate production of IB4tetΔNIκBα expressing ΔNIκBα at indicated time points. The percent change over uninduced cells is presented (n=3; mean±s.d. *p<0.05 /** p<0.005). (B) Cell survival (% Annexin V−, Propidium Iodide−) of ΔNIκBα expressing cells grown in normal media with or without supplemental Glutamine (L-Q;22mM) and α-ketoglutarate (α–keto;20mM), (day 5, n=8; mean+s.d., **p<0.005). (C) Autophagosome marker LC3b localization (green) and DNA (blue) in ΔNIκBα- and ΔNIκBα+ IB4tetΔNIκBα grown with QVD (10uM) with or without supplemental glutamine and α-ketoglutarate (72h). Bar=10μm. (D) Whole cell lysates corresponding to (C) were analyzed for LC3b-I and autophagosome associated LC3b-II expression. TRAF1 and GAPDH served as controls for NFκB activity and loading respectively. (E) Cell survival (high forward scatter, low side scatter) after autophagy inhibition with 3-methyladenine (3MA). IB4tetΔNIκBα were cultured ΔNIκBα-(black),ΔNIκBα+ (white), or ΔNIκBα+ with supplemental glutamine and α-ketoglutarate (grey). After 48h the indicated concentrations of 3MA were added for an additional 18–24h. Percent cell survival was normalized to non 3MA treated cells (n=3; mean±s.d.); ΔNIκBα-= 89%; ΔNIκBα+ = 69%; ΔNIκBα+ & L-Q/α-keto= 81%. (F) Model: Impact of NFκB transcription on metabolism.