Fig. 1.
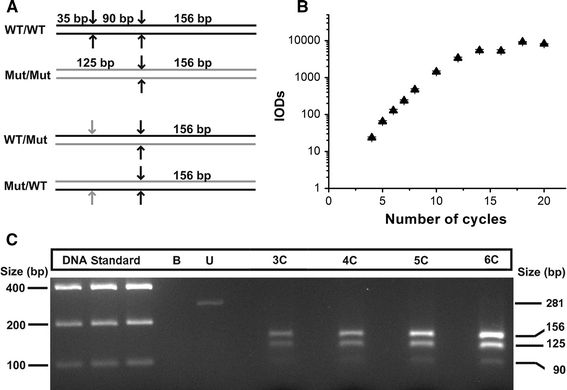
Experimental approach to minimize heteroduplex formation. a Schematic representation of restriction fragments produced by Nde II digestion of wild-type and mutated homoduplexes for mutation R723G (upper panels). Formation of heteroduplexes (lower two panels) generates one refractory restriction site (gray arrows), thus producing the 125-bp fragment from both strands of the heteroduplexes. b For reconditioning PCR, after 35 PCR cycles 1:100 dilutions of the product were subjected to another PCR and quantified after each cycle. The reaction was exponential until the seventh cycle. IOD, integrated optical density (SD from densitometric analysis at different exposure times). c 3.5% agarose gel with restriction digests of PCR products of a sample from the left ventricular lateral wall of a patient heterozygous for mutation R723G. The 35-bp fragment is not seen due to its small size. Cleavage of the reconditioning PCR products of three, four, five or six cycles (lanes 3C–6C) yielded mutated MYH7-mRNA fractions of 73, 82, 77 and 75%, respectively (on average 74 ± 8% in this muscle sample). There was no indication for heteroduplex-induced increase of mutated MYH7-mRNA at increasing cycle numbers. Lanes 1–3 12, 15 and 18 μl of equimolar DNA standard; B blank; U undigested PCR product
