Abstract
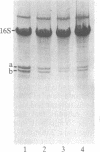
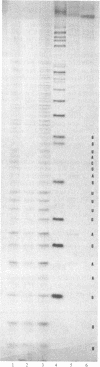
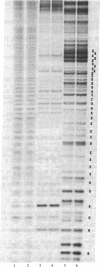
A nine-base DNA oligomer [d(GTATCTAAT)] was used to probe the accessibility and function of bases in the region 787-795 of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA. Hybridization of the cDNA [d(GTATCTAAT)] to 16S rRNA in situ was carried out by binding the probe to intact 30S ribosomal subunits. Nitrocellulose filter binding showed that cDNA hybridization saturated with increasing probe concentration, suggesting that the probe was binding to a discrete site or sites. RNase H digestion of the rRNA under the DNA . rRNA hybrid and sequencing of the resultant RNA fragments verified that the cDNA probe bound specifically to the 787-795 region. Hybridization experiments using the cDNA probe showed that bases in the 787-795 region of 16S rRNA are exposed on the surface of 30S subunits. The functional role of bases 787-795 was then tested by assaying various ribosomal activities with the cDNA in place. Results of these functional assays demonstrate that this 16S rRNA region is directly involved in the association of 30S and 50S subunits.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backendorf C., Ravensbergen C. J., Van der Plas J., van Boom J. H., Veeneman G., Van Duin J. Basepairing potential of the 3' terminus of 16S RNA: dependence on the functional state of the 30S subunit and the presence of protein S21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1425–1444. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta A., Kuechler E. Part of the 23S RNA located in the 11S RNA fragment is a constituent of the ribosomal peptidyltransferase centre. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 14;163(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80844-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta A., Steiner G., Brosius J., Noller H. F., Kuechler E. Identification of a site on 23S ribosomal RNA located at the peptidyl transferase center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3607–3611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Noller H. F. Protection of ribosomal RNA from kethoxal in polyribosomes. Implication of specific sites in ribosome function. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):27–46. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H. 5'-32P labeling of RNA and DNA restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Protection of specific sites in 16 S RNA from chemical modification by association of 30 S and 50 S ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 5;109(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Site specific enzymatic cleavage of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):179–192. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A., Wagner R. Comparison of Escherichia coli tRNAPhe in the free state, in the ternary complex and in the ribosomal A and P sites by chemical probing. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):261–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. J., Zeller M. L., Thurlow D. L., Gourse R. L., Stark M. J., Dahlberg A. E., Zimmermann R. A. Interaction of ribosomal proteins S6, S8, S15 and S18 with the central domain of 16 S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Mechanism of ribosomal subunit association: discrimination of specific sites in 16 S RNA essential for association activity. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 5;130(4):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Noller H. F. Protection of specific sites in 23 S and 5 S RNA from chemical modification by association of 30 S and 50 S ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 5;130(4):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Rossetti G. P., Van Holde K. E. Physical studies of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 14;44(2):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin A. S., Skripkin E. A., Chichkova N. V., Kopylov A. M., Bogdanov A. A. An enzymatic approach for localization of oligodeoxyribonucleotide binding sites on RNA. Application to studying rRNA topography. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Chaires J. B. Functional modification of 16S ribosomal RNA by kethoxal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3115–3118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Capel M., Kjeldgaard M., Engelman D. M., Moore P. B. Positions of proteins S14, S18 and S20 in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):265–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santer M., Shane S. Area of 16S ribonucleic acid at or near the interface between 30S and 50S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):900–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.900-910.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz I., Ofengand J. Photochemical cross-linking of unmodified acetylvalyl-tRNA to 16S RNA at the ribosomal P site. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2524–2530. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam M. F., Hill W. E. Physical characteristics of the reconstitution intermediates (RI30 and RI30*) from the 30S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 27;20(22):6480–6484. doi: 10.1021/bi00525a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir A., Miskin R., Vogel Z., Elson D. The inactivation and reactivation of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:406–426. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]