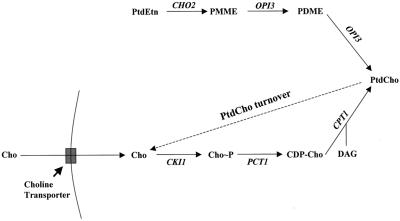
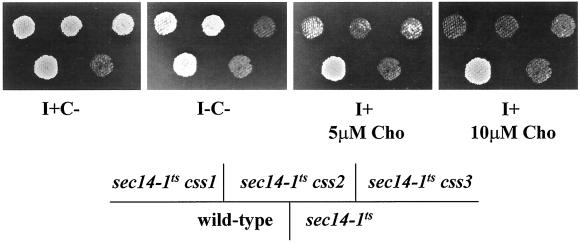
Figure 1.
(A) The two pathways for PtdCho biosynthesis in yeast. Mutations in CDP-choline pathway, but not in PtdEtn-methylation pathway, suppress the essential requirement of Sec14p for Golgi secretory function and cell viability. CDP-choline pathway activity is supported by endogenous choline derived from PtdCho turnover, and by exogenous choline, which is captured by the choline transporter. In the absence of exogenous choline, PtdCho turnover represents the sole pathway for choline production. Genetic designations for the structural genes encoding enzymes for PtdCho synthesis and turnover are given at the corresponding execution points. The role of the choline transporter is also illustrated. (B) Choline-sensitive suppressors of sec14 (css). Indicated strains were patched on YPD plate and incubated at 26°C for 24 h. The cell patches were then replica plated onto minimal plates supplemented with 1 mM inositol but no choline (I+C−), or with 1 mM inositol and choline at indicated concentrations (I+ 5 μM Cho and I+ 10 μM Cho), or neither inositol nor choline (I−C−). The replica plates were then incubated at 37°C for 48 h. Isogenic strains were used: CTY182 (wild-type), CTY1-1A (sec14-1ts), CTY1374 (sec14-1ts css1), CTY1375 (sec14-1ts css2), CTY1473 (sec14-1ts css3).