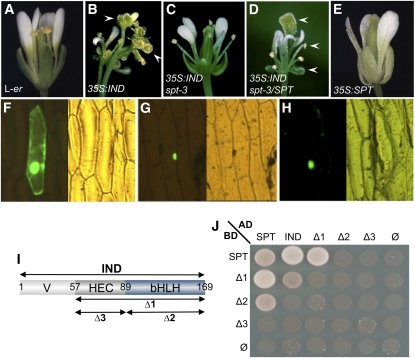
Figure 2.
Ectopic IND Function Is SPT-Dependent, and IND and SPT Proteins Interact.
(A) to (E) Flowers of L-er (A), 35S:IND (B), 35S:IND spt-3 (C), 35S:IND spt-3/SPT (D), and 35S:SPT (E). Plants in (C) and (D) derive from the same transformation event. Arrowheads in (B) and (D) indicate ectopic stigma.
(F) to (H) GFP localization in epidermal onion cells transiently transformed with 35S:SPTΔNLS:GFP alone (F), 35S:SPT (G), or 35S:IND (H).
(I) Schematic of IND truncated versions used in (J). Variable N-terminal domain (V), the HEC-conserved domain (HEC), and the bHLH domain (bHLH) are indicated. Amino acid positions are shown. Δ1 construct contains HEC and bHLH domain, Δ2 contains the bHLH domain and Δ3 contains the HEC domain.
(J) Yeast two-hybrid experiment using fusions of SPT and IND (full-length and truncated version) with GAL4 activation and binding domains (AD and BD, respectively). Cells were spotted on selective medium lacking Leu, Trp, His, and adenine.