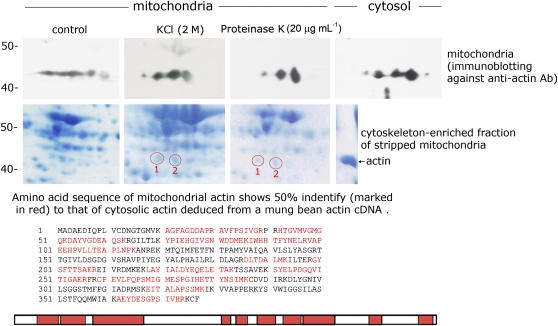
Figure 3.
Mitochondrial Actin Possesses a Similar Amino Acid Sequence Compared with Cytosolic Actin and Was Identified by LC-MS/MS.
The top panel shows the immunoblot analysis with an antiactin antibody on a 2D gel of separated total mung bean seedling mitochondrial proteins (control [no treatment] or mitochondria treated with 2 M KCl or 20 μg mL−1 proteinase K) and total cytosolic protein. The middle panel shows the Coomassie blue–stained 2D gel fractionation profile of cytoskeleton-enriched fractions isolated from control mitochondria, 2 M KCl-treated mitochondria, and 20 μg mL−1 proteinase K–treated mitochondria (see Methods). Spots 1 and 2 were preidentified as actin based on immunoblot results shown in the top panel. The bottom panel shows the LC-MS/MS analysis of the amino acid sequence of spot 1 in the KCl-treated mitochondria shown in the middle panel. The same amino acid sequence was also found in spot 2 of KCl-treated mitochondria and in spots 1 and 2 of proteinase K–treated mitochondria. The amino acid sequence was compared with an amino acid sequence deduced from the mung bean actin cDNA sequence that we reported previously. The sequences marked in red are the identical sequence fragments between mitochondrial actin and cytosolic actin deduced from a mung bean actin cDNA.