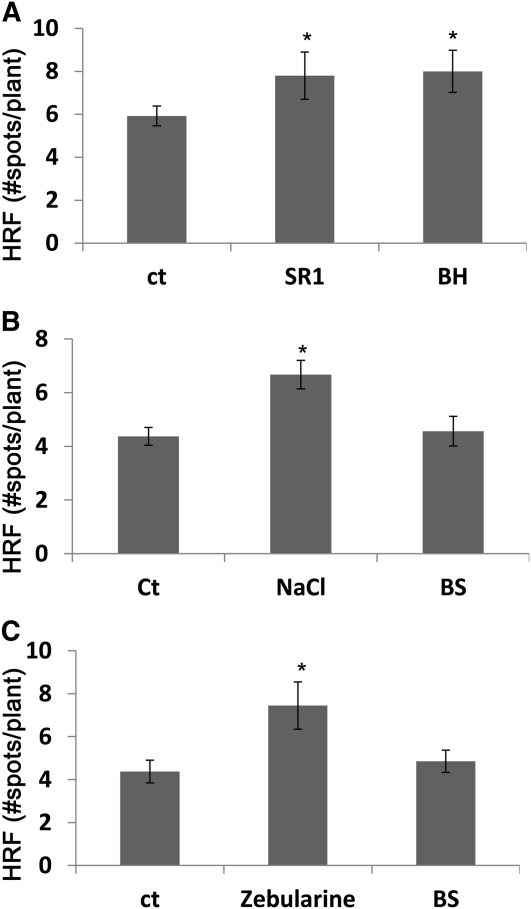
Figure 6.
Changes in HRF in Bystander Plants Exposed to Volatiles from Plants Treated with Necrotizing or Non-Necrotizing Types of Stress.
(A) HRF in bystander tobacco plants exposed to volatiles from TMV-infected tobacco. Two leaves of 4-week-old tobacco plants (cultivars SR1, susceptible to TMV, or Big Havana [BH], resistant to TMV) were infected with 200 ng of TMV. Infected SR1 or Big Havana plants were placed in a sealed bag side by side with naive tobacco plants of the same cultivar. Each experimental point consisted of three pots with 8 to 12 plants per pot. Bars represent the average HRF ± sd calculated from three biological repeats. Asterisks indicate a significant difference compared with control (ct) (P < 0.05).
(B) HRF in Arabidopsis plants exposed to NaCl or to volatiles from NaCl-treated plants (BS). Two-week-old Arabidopsis plants were grown on soil and watered with 250 mM NaCl for 2 d, after which they were placed side by side with naive Arabidopsis plants in sealed plastic bags for 4 d. At day 4 after exposure, bags were opened and HRF was measured 3 d later (7 d after treatment). Each experimental point consisted of three pots with 12 to 20 plants per pot. Bars represent the average HRF ± sd calculated from three biological repeats. Asterisks indicate a significant difference compared with control (P < 0.05).
(C) HRF in Arabidopsis plants exposed to zebularine or to volatiles from zebularine-treated plants (BS). Two-week-old Arabidopsis plants grown on soil were sprayed with zebularine and immediately placed side by side with naive Arabidopsis plants in sealed plastic bags for 4 d. At day 4 after exposure, bags were opened and HRF was measured 3 d later (7 d after treatment). Experimental details are the same as in (B). Asterisks indicate a significant difference compared with control (P < 0.05).