Figure 1.
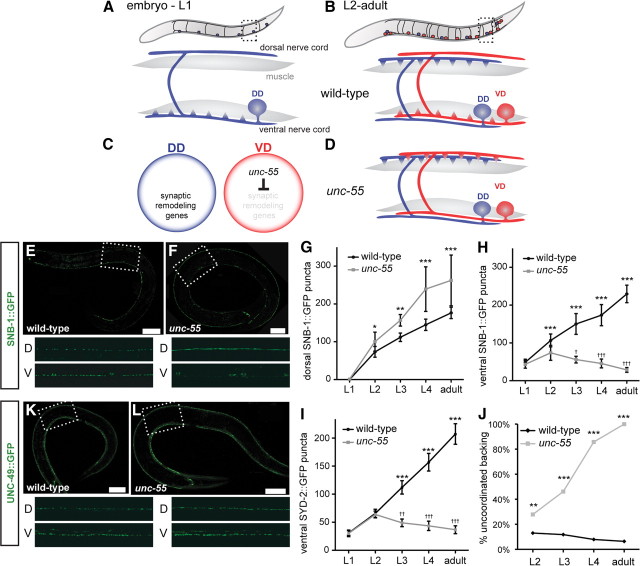
Synaptic remodeling in wild-type and unc-55 GABAergic motor neurons. For all panels, dorsal is up and anterior is to the left. A, Embryonic DD motor neurons (blue) extend an anterior ventral process and commissure to the dorsal nerve cord; NMJs are established with ventral muscles. B, Toward the end of L1 larval period, ventral DD motor neuron NMJs are removed and new NMJs are assembled in the dorsal DD process. Postembryonic VD motor neurons (red) are born during this stage and adopt ventral NMJs. C, UNC-55 is selectively expressed in VD motor neurons to block synaptic remodeling. D, VD motor neurons remodel ectopically in unc-55 mutants and adopt dorsal NMJs. E–H, The synaptic vesicle marker, SNB-1::GFP, marks GABAergic motor neuron NMJs. Scale bars: 20 μm; inset panels, 50 μm. E, SNB-1::GFP puncta are visible in both dorsal (DD motor neurons) and ventral (VD motor neurons) adult nerve cords. F, In unc-55 mutants, ventral SNB-1::GFP puncta are depleted, whereas the number of dorsal SNB-1::GFP puncta increases. G, H, Quantification of SNB-1::GFP puncta in dorsal and ventral nerve cords throughout development. n ≥ 10 for each genotype at each stage. Error bars indicate SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for wild-type versus unc-55 in two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-comparison test. G, Dorsal SNB-1::GFP puncta are more numerous in unc-55 mutants than wild type due to ectopic remodeling of VD motor neurons. H, Ventral SNB-1::GFP puncta are more numerous in wild type than in unc-55 mutants. Ventral SNB-1::GFP puncta are significantly depleted during development in unc-55 mutants, indicating that VD motor neurons initially establish ventral NMJs in the L2 and then remodel to favor dorsal outputs in the adult. †p < 0.05, †††p < 0.001, L2 versus L3, L4, or adult for one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-comparison test. I, Quantification of SYD-2::GFP puncta, which marks the presynaptic apparatus, in the ventral nerve cord throughout development. SYD-2::GFP localization in unc-55 is indistinguishable from wild type at the L2 stage, but ventral SYD-2::GFP puncta are depleted as VD motor neurons remodel during development. n ≥ 10 for each genotype at each stage. Error bars indicate SD. ***p < 0.001 for wild-type versus unc-55 in two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-comparison test; ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001, L2 versus L3, L4, or adult for one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-comparison test. J, VD motor neurons initially form ventral neuromuscular junctions in unc-55 as indicated by movement similar to wild type at younger stages, but we observe a progressive increase in uncoordinated movement as the animal ages and VD motor neurons remodel. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for wild-type versus unc-55, Fisher's exact test; n ≥ 100 for each genotype at each stage. K, L, GABA receptor localization in muscle is not perturbed by VD motor neuron synaptic remodeling. GABA receptor (UNC-49::GFP) localization in body wall muscle (K) is normal in unc-55 adults (L), suggesting that L2 unc-55 VDs initially form functional ventral synapses. Scale bars: 20 μm; inset panels, 50 μm.