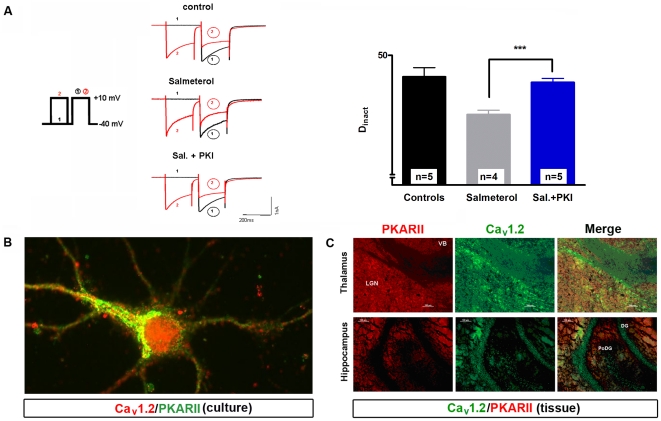
Figure 5. Inhibition of PKA completely suppresses the effect of βAR stimulation on CDI in TC neurons.
(A) Representative current traces recorded under control conditions (upper left panel) and in the presence of the specific β2AR agonist salmeterol alone (10 µM; left middle panel) or in combination with PKI 14–22 amide (10 µM; lower left panel). The bar graph represents Dinact under different recording conditions (as indicated). The mean value of five cells recorded under control conditions was taken for comparison with four cells recorded under 10 µM salmeterol and five cells recorded under 10 µM salmeterol plus PKI 14–22 amide. Data are presented as means ± SEM of several independent experiments. ***P<0.001. Significance of salmeterol plus PKI (n = 5) versus salmeterol alone (n = 4) was calculated by Student's t test. The degree of inactivation is given by the normalized current amplitude of the mean postpulse I/V at +10 mV. (B) Close co-expression of the main modulator of CDI, PKA (green) and CaV1.2 (red) in cultured neurons. Yellow dots represent places were these two proteins are in close proximity. Data shown are representative pictures from several independent immunostainings and preparations of neurons. In all cases, omission of primary antibodies resulted without signal (negative control). (C) Indicated brain regions were immunostained with antibodies specific for PKARIIβ and CaV1.2. Thalamic regions LGN and VB revealed very strong interaction patterns in merged pictures. Association of these proteins is still present in hippocampus but on lower level. DG (dentate gyrus), PoDG (polymorph layer of the dentate gyrus).