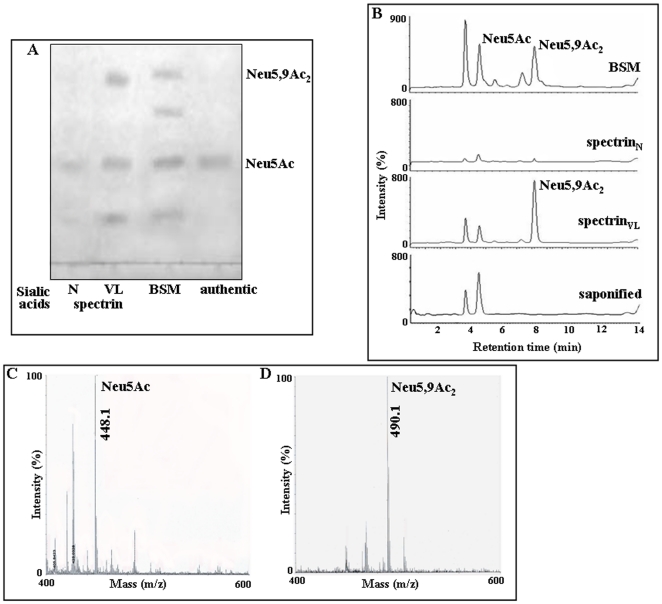
Figure 6. Presence of Neu5Ac and Neu5,9Ac2 in spectrinVL by analytical methods.
A. Thin layer chromatography (TLC). Glycosidically bound sialic acids of spectrinVL were subjected to acid hydrolysis, purified, separated on a TLC plate and detected by staining with orcinol/HCl spray reagent and baking at 180°C. Similarly processed free sialic acids released from BSM served as standard. Additionally, commercially available Neu5Ac was used as references. For comparison liberated sialic acids from purified spectrinN were similarly analyzed. B. Enhanced presence of Neu5Ac and Neu5,9Ac2 in spectrinVL as determined by fluorimetric HPLC. Glycosidically bound sialic acids released from spectrinVL by acid hydrolysis were derivatized with DMB and analyzed by fluorimetric HPLC before and after saponification as described in Materials and Methods. A representative chromatogram of the spectrinVL and spectrinN derived sialic acids showed the presence of fluorescent derivatives of free sialic acids. In parallel sialic acids of BSM similarly analyzed under identical conditions served as standard. C–D. Identification of sialic acids by MALDI-TOF MS. Fractions corresponding to peaks of Neu5Ac (C) and Neu5,9Ac2 (D) were collected after fluorimetric HPLC, spotted and analyzed by MALDI-TOF MS using DHBA matrix as described in Materials and Methods. Positive ion mode was used for mass-spectrometric analysis with 1000 laser shots per spot.