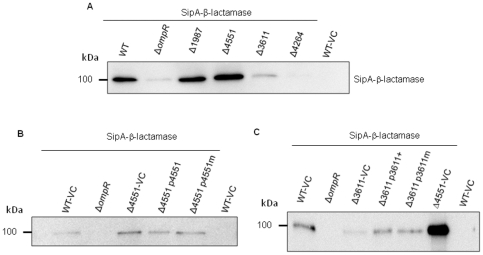
Figure 3. GG(D/E)EF/EAL domain proteins affect secretion of the SipA effector protein.
(A) Mutants of the diguanylate cyclases STM1987 and STM4551 show enhanced secretion of a SipA-β-lactamase fusion protein, while secretion was diminished in mutants of the phosphodiesterases STM3611 and STM4264. (B) Enhanced secretion of the SipA-β-lactamase fusion protein in the STM4551 mutant is restored by expression of STM4551 from plasmid pBAD30 and by expression of the catalytically inactive STM4551E267A mutant. (C) Diminished secretion of the SipA-β-lactamase fusion protein in the STM3611 mutant is restored by expression of STM3611 from plasmid pBAD30 and by expression of the catalytically inactive STM3611K179A mutant. Positive control = Δ4551-VC. SipA-β-lactamase indicates chromosomal fusion in respective strains. Detection of the SipA-β-lactamase fusion protein by western blot analysis using an anti-β-lactamase antibody. Strain S. typhimurium UMR1 with pBAD30 expressing β-lactamase in the periplasm (WT-VC) served as β-lactamase secretion control. WT = wild type S. typhimurium UMR1; ΔompR, negative control; VC = vector control pBAD30.