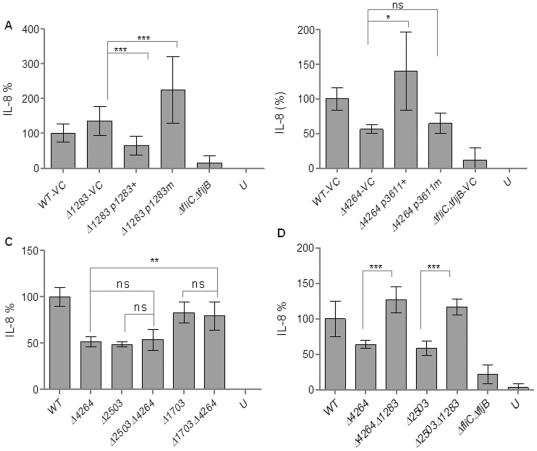
Figure 8. Complementation of the IL-8 induction phenotype of GG(D/E)EF/EAL protein mutants and double mutant analysis.
(A) Complementation of the STM1283 mutant with STM1283 (p1283+) and STM1283D425A (p1283m) demonstrates requirement of the di-guanylate cyclase activity of STM1283 for complementation of the IL-8 induction phenotype as the enhanced IL-8 induction rate exhibited by the STM1283 mutant was significantly reduced by complementation with wild type STM1283, but not with the non-functional mutant STM1283D425A with the GGDEF motif altered to GGAEF. (B) Complementation of the STM4264 mutant with STM3611 (p3611+) and STM3611K179A (p3611m) demonstrates requirement of the phosphodiesterase activity of STM4264 for complementation of the IL-8 induction phenotype. The reduced IL-8 induction rate exhibited by the STM4264 mutant was increase to wild type levels by complementation with the EAL-only protein STM3611, but not with the catalytically inactive mutant STM3611K179A. (C) No additive effect on the reduction of IL-8 production is observed when double mutants of STM2503/STM4264 and STM1703/STM4264 were compared to the respective single mutants. (D) Deletion of the gene encoding the phosphodiesterase STM4264 or the putative phosphodiesterase STM2503 has no effect on IL-8 expression in the STM1283 mutant background indicating that STM4264 and STM2503 degrade the c-di-GMP produced by the di-guanylate cyclase STM1283. WT = wild type S. typhimurium UMR1; VC = vector control pBAD30; ΔfliCΔfljB, negative control, U = unstimulated HT-29 cells. Bars show mean ± standard deviation from at least three independent biological experiments performed in two technical replicates. Statistical significance is indicated by *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 as compared with the respective single mutant.