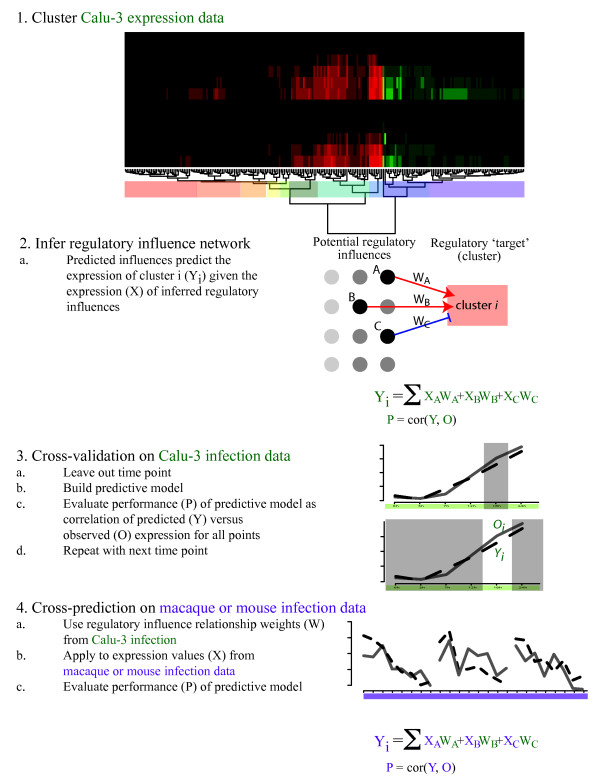
Figure 3.
Overview of cross-predictive modeling approach. To allow cross-predictive comparison of response to influenza infection between Calu-3 and in vivo systems, we first clustered the Calu-3 expression data (1) from two similar experiments using hierarchical clustering. The clusters (colored boxes) are used to summarize system behavior and serve as the 'targets' for inference. A regulatory influence network is inferred (2) that relates the expression of inferred regulatory influences (X) to the mean expression (Y) of each target cluster (i). Cross-validation (3) is carried out by leaving out expression data from each time point in turn, inferring a model, then using the model to predict the behavior of each cluster for the left out time point. Performance of the model is assessed as the gene-weighted mean correlation between the predicted (Y) and observed (O) expression of all clusters. Finally, the weights from the Calu-3 model are applied to the macaque/mouse data and performance assessed by evaluating the gene-weighted mean correlation between the predicted expression and the observed expression in macaque/mouse for each cluster.