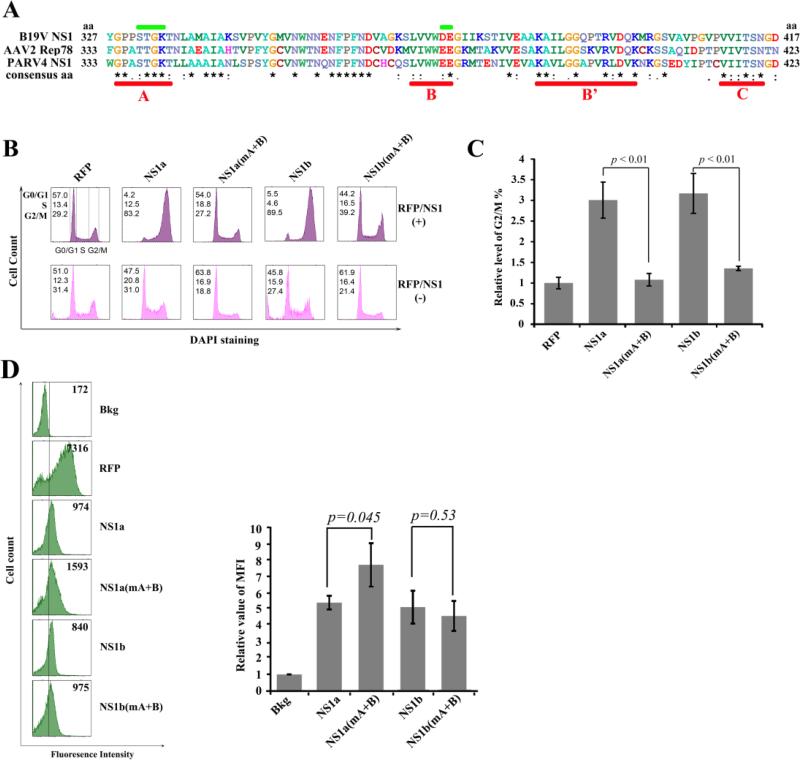
Figure 6. The helicase motifs of the PARV4 NS1 are responsible for G2/M arrest induced by PARV4 NS1 protein.
(A) Comparison of the NS1 helicase motifs. The amino acid sequences of B19V NS1, AAV2 Rep78, and PARV4 NS1 were aligned using ClustalW2 (Larkin et al., 2007). The alignment of aa 327-417 of B19V NS1, aa 333-423 of AAV2 Rep78, and aa 333-423 of PARV4 NS1 is depicted with identical amino acids shown by the asterisk, while homologous amino acids are shown as two dots under the amino acid. Conserved motifs (Walker boxes A, B, B’, and C) are underlined in red, while the mutated regions of boxes A and B are marked in green. (B&C) PARV4 NS1 protein induces G2/M arrest. (B) CD34+ HSCs were transduced with lentiviruses to express proteins as indicted. At 48 hrs post-transduction, RFP- or NS1-expressing cells were selectively gated for anti-Flag staining, followed by DAPI staining for cell cycle analysis. The cell cycle patterns of both NS1/RFP-positive and NS1/RFP-negative cells are shown in parallel. In each panel, the percentages of cells in the G1, S, and G2/M phases are indicated, respectively (top left). A representative experiment is shown. (C) The percentage of RFP-expressing cells in G2/M was arbitrarily set as 1. Relative values are shown with average and standard deviation from at least three independent experiments. P values were determined using a student's t test. (D) Expression levels of PARV4 NS1 proteins. The expression levels of RFP and NS1 as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) were analyzed by flow cytometry in lentivirus-transduced (NS1/RFP+) cells at 48 hrs post-transduction. The reference line is selected arbitrarily to show the relative position of the NS1/RFP-positive and negative peaks, and Bkg (background) represents the secondary antibody only control. A representative experiment is shown to the left. Relative MFI values were determined as fold changes of MFI of NS1/RFP+ cells compared to that of Bkg, and are shown to the right with average and standard deviation.