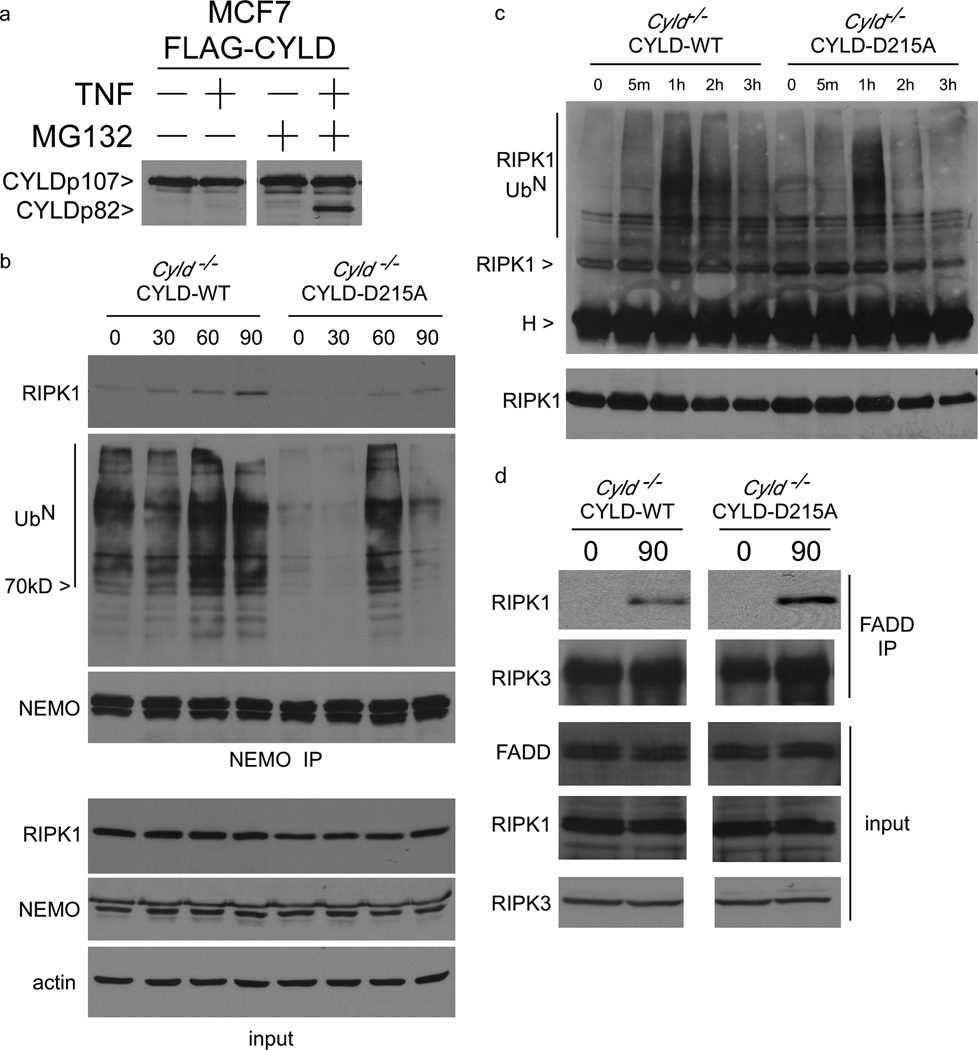
Figure 5. CYLD-D215A switches pro-survival NEMO-RIPK1 complex to pro-necrotic RIPK1-FADD complex.
(a) MCF7 cells stably expressing FLAG-CYLD-WT were treated with vehicle or 25µM MG132 for one hour and then stimulated with 100 ng/ml TNF for 5 hours. Cytoplasmic lysates were blotted with antibody against the C-terminus of CYLD. (b) NEMO was immunoprecipitated from Cyld−/− MEFs reconstituted with CYLD-WT or CYLD-D215A after TNF stimulation for different periods of time. The NEMO protein complex was sequentially immunoblotted with anti-RIPK1 to detect the pro-survival NEMO-RIPK1 complex, and with anti-ubiquitin to detect the level of ubiquitinated protein in the NEMO complex. Corresponding whole cell lysates were blotted with for RIPK1, NEMO and actin in the lower three panels. (c) RIPK1 was immunoprecipitated from CYLD-WT and CYLD-D215A-expressing MEFs after stimulation with TNF for different periods of time in high stringency buffer. The immunoprecipitates were blotted with anti-ubiquitin to detect ubiquitinated RIPK1. (d) FADD immunoprecipitates from CYLD-WT and CYLD-D215A-expressing MEFs stimulated for 90 minutes with TNF were immunoblotted for the presence of RIPK1. Samples of the lysates were also immunoblotted for RIPK1, RIPK3 and FADD.