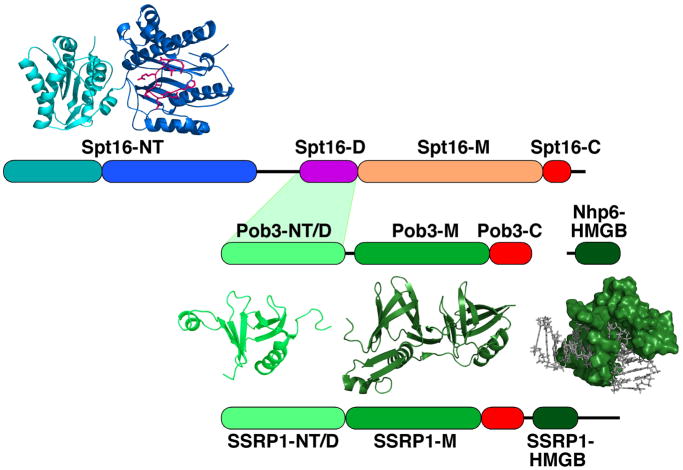
Figure 1.
Domain structure of FACT proteins.
The NT (N-terminal), D (dimerization), M (middle), C (C-terminal), and HMGB domains of S. cerevisiae Spt16, Pob3, and Nhp6 and human SSRP1 are diagrammed to scale. The acidic domains are colored red. SSRP1 has a serine-rich C-terminal extension not found in yeast or fungal FACT. The Spt16-NT domain has two lobes as indicated in cyan and blue, with the loop enclosing the conserved putative peptide-binding domain indicated in magenta [30, 31]. Ribbon diagrams of the domains whose crystallographic structures are known are shown, as is a surface representation of Nhp6 bound to DNA determined by NMR [90]. Structures were rendered in PyMOL using PDB files 3BIQ (Spt16-NT) [31], 3F5R (Pob3-NT/D) [35], 2GCL (Pob3-M) [12], and 1J5N (Nhp6-DNA) [90].