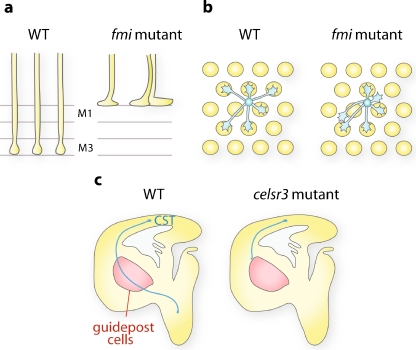
Fig. 2.
Examples of Fmi/Celsr phenotypes in axon guidance and targeting. a In the Drosophila visual system, R8 photoreceptor axons are arranged in evenly spaced topographic arrays and target the M3 layer in the medulla. In fmi mutants, competitive axon–axon interactions are lost leading to an axon bundling phenotype. Moreover, R8 axons stop prematurely at the M1 layer due to impaired Fmi homophilic axon–target interactions. b Photoreceptor axons arrive in the fly lamina as an ommatidial bundle. Axons defasciculate and grow perpendicularly to the bundle in stereotyped directions to reach their correct target. In fmi mutants, axons make directional errors and innervate inappropriate targets. Adapted from [2]. c In mice, several axon tracts of the internal capsule are misguided in Celsr3 mutants, including subcerebral projections (CST, blue). These tracts are defective when Celsr3 is absent in these axons or in guidepost cell (red area), suggesting that Celsr3 regulates axon guidance via homophilic interactions. Adapted from [31]