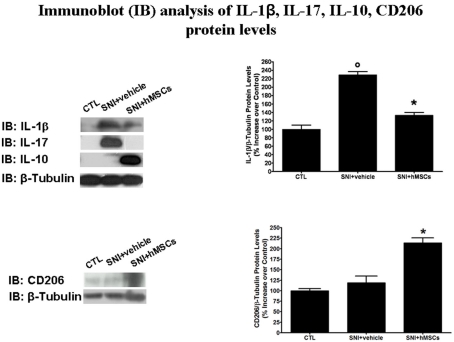
Figure 3.
Representative western blot analysis for IL-1β, IL-17, IL-10, CD206, and housekeeping β-tubulin mouse proteins are shown. The semi-quantitative analysis of protein levels was carried out by the “Gel Doc 2000 UV System” (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Human MSC treatment (on day 4 after SNI surgery) reduced the protein levels of pro-inflammatory interleukins IL-1β and IL-17 in hMSC-treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + hMSCs) respect to vehicle treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + vehicle). Human MSC treatment (on day 4 after SNI surgery) increased the protein levels of anti-inflammatory interleukin IL-10 and activated anti-inflammatory macrophage marker CD206 in hMSC-treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + hMSCs) respect to vehicle treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + vehicle). Upper graph shows IL-1β/β-tubulin normalized values as obtained by immunoblot analysis. Human MSC treatment (on day 4 after SNI surgery) reduced the protein levels of IL-1β interleukin in hMSC-treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + hMSCs) respect to vehicle treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + vehicle). ANOVA, followed by Student–Neuman–Keuls post hoc test, was used to determine the statistical significance among groups. *p < 0.01 was considered statistically significant. Lower graph shows CD206/β-tubulin normalized values as obtained by immunoblot analysis. Human MSC treatment (on day 4 after SNI surgery) increased the protein levels of activated anti-inflammatory macrophage marker CD206 in hMSC-treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + hMSCs) respect to vehicle treated 30 days-neuropathic mice (SNI + vehicle). ANOVA, followed by Student–Neuman–Keuls post hoc test, was used to determine the statistical significance among groups. *p < 0.01 was considered statistically significant.