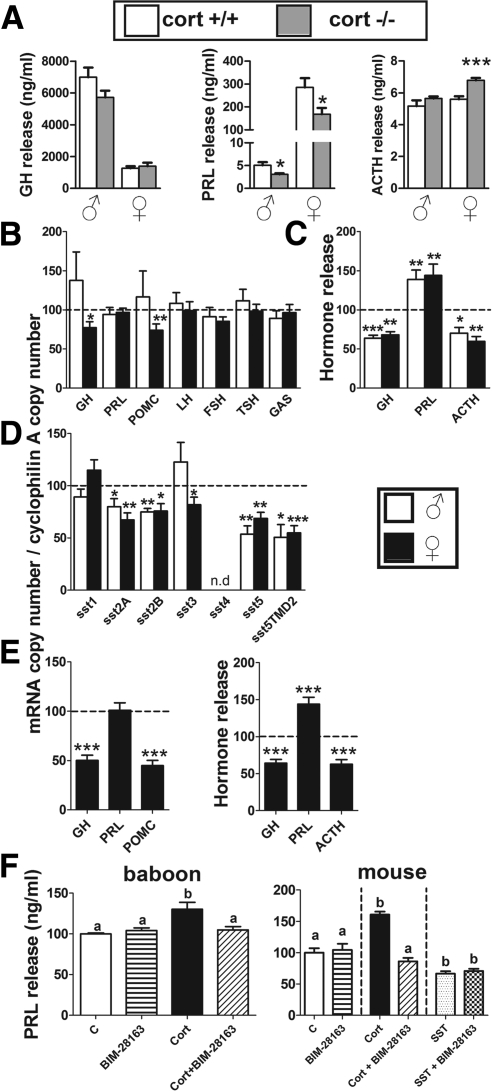
Fig. 3.
Direct effect of CST or lack of endogenous CST on pituitary hormonal expression and secretion of male/female mice and female baboons. A, GH, PRL, and ACTH release levels (24-h culture; ng/ml) in primary pituitary cell cultures of male and female cort+/+ (white columns) and cort−/− (gray columns) mice under basal condition. B, Effect of CST-14 (100 nm, 24 h) on GH, PRL, POMC, LH, FSH, TSH, and GAS expression on primary pituitary cell cultures of male (white columns) and female (black columns) wild-type (cort+/+) mice. C, Effect of CST-14 (100 nm, 24 h) on GH, PRL, and ACTH release on primary pituitary cell cultures of male (white columns) and female (black columns) wild-type (cort+/+) mice. D, Effect of CST-14 (100 nm, 24 h) on SST receptors isoforms/variants (sst) on primary pituitary cell cultures of male (white columns) and female (black columns) wild-type (cort+/+) mice. E, Effect of CST-17 (100 nm, 24 h) on GH, PRL, and POMC expression (left) and on GH, PRL, and ACTH release (right) in primary pituitary cell cultures of female baboon. F, Effect of 100 nm CST-17 (in baboons; 100 nm), 1 μm CST-14, or 100 nm SST-14 (in mice) (24 h) alone or in combination with BIM-28163 (GHS-R1a antagonist; 10 nm) on PRL release in primary pituitary cell cultures of female baboon and mice [vehicle-treated control (C) was set at 100%]. Values are represented as the means ± sem of three to four independent experiments (three to five wells/treatment per genotype/gender) and in B–E are expressed as percentage of vehicle-treated controls (shown by the dotted line set at 100%). Asterisks (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001) indicate values that differ from the corresponding controls within genders (from vehicle-treated controls for B–E and from cort+/+ within genders for A). In F, values that differ significantly (P < 0.05) are designated by different letters (a and b).