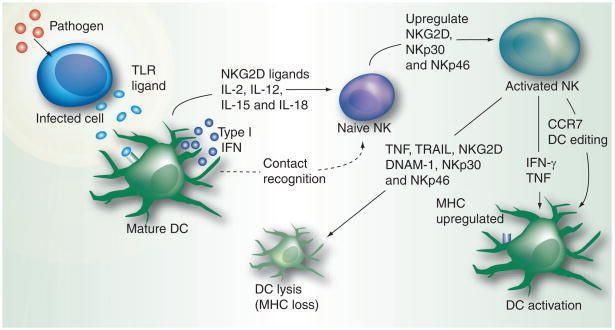
Figure 3. NK–dendritic cell cross-talk.
The TLR ligands secreted by an infected cell are captured by the DCs, the professional antigen-presenting cells. This stimulates the DCs to produce type I interferon through the IRF-3 and IRF-7-mediated JAK–STAT pathway. IL-2, IL-15 and other cytokines presented by the DC to naive NK cells, together with type I interferons, activate the naive NK cells and stimulate their activation and proliferation. NK cells, in turn, regulate the functioning of DCs by eliminating immature DCs with low MHC expression through various effector pathways. Mature DCs with an upregulated expression of MHC are not affected by such pathways; instead, they undergo further activation.
DC: Dendritic cell; DNAM: DNAX accessory molecule; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.