Figure 2. Mucin mediated cellular signaling events in breast cancer. MUC1-ICAM1 interaction.
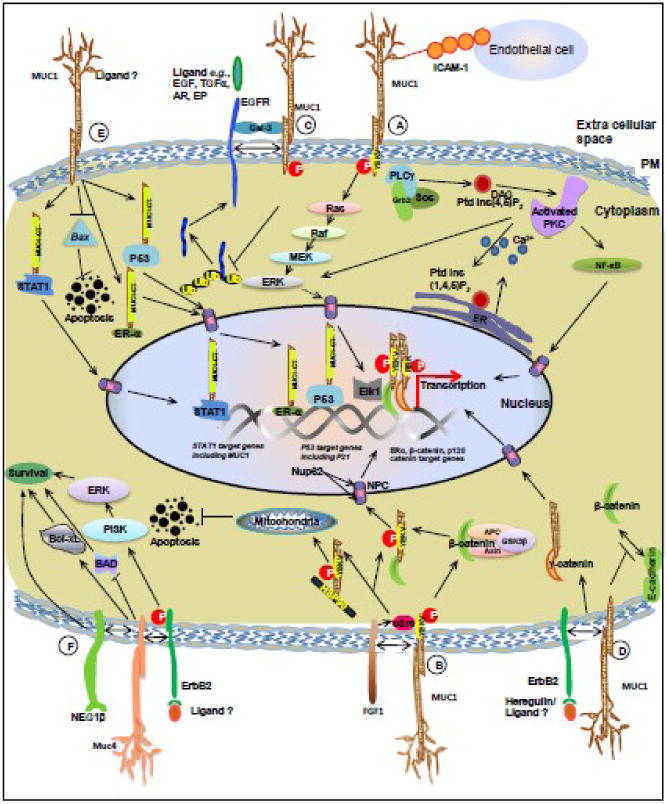
MUC1–ICAM-1 interactions regulate different heterotypic cell– cell adhesions. Phosphorylated MUC1-CT can contribute to Grb2–Sos-mediated activation of the Ras–ERK pathway or activation of phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ)-mediated signaling events. (B) MUC1-FGF1 interaction: FGF1 induces phosphorylation of the MUC1-CT on the YEKV motif via activation of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase c-Src which results in nuclear translocation of MUC1-CT to drive the transcription of β-catenin, estrogen receptor α (ERα) and p53 target genes. The MUC1-CT–HSP70/HSP90 interaction facilitates translocation of MUC1-CT to mitochondria, and attenuates activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in the response to stress. (C) MUC1-EGFR interaction: MUC1 binds to ErbB1 (EGFR) following activation by EGF. This interaction is bridged by the secreted glycoprotein galectin-3. The interaction (between MUC1 and EGFR) inhibits EGF-stimulated ubiquitination and internalization of ErbB1, thus driving EGF-mediated downstream signaling events. (D) MUC1-HER2 interaction: Stimulation of BC cells with heregulin (HRG), a soluble ligand for HER2, leads to phosphphorylation of the MUC1-CT (at the YEKV motif). The phosphorylated MUC1-CT interacts with molecules such as γ-catenin and p120 catenin, following which the complex is translocated into the nucleus by Nup62, a nucleoprotein located on the nuclear pore. (E) Nuclear localization of MUC1-CT: The MUC1-CT interacts with the nucleoprotein Nup62, an interaction that regulates the transport of the MUC1-CT into the nucleus. In the nucleus, the MUC1-CT interacts with and regulates transcription of ERα, β-catenin, p120 catenin, STAT1 and p53 target genes. (F) MUC4 mediated cell signaling in breast cancer cells: MUC4 can bind to the receptor tyrosine kinase HER2 and alter its cellular signaling by activation of the PI3-kinase and Erk pathways. MUC4 induced phosphorylation of HER2 leads to the inactivation of pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bad and an increase in expression of pro-survival proteins like Bcl-xL. (Abbreviations: Gal-3-Galectin -3, NPC-Nuclear Pore Complex, MUC1-mucin 1, MUC4-mucin 4, DAG-diacylglycerol, ER- endoplasmic reticulum, NF-kB- nuclear factor kB; PKC-protein kinase C, PM- plasma membrane, EGF-Epidermal Growth Factor, TGFβ-Transforming Growth Factor β, AR-Amphiregulin, EP-Epiregulin).
