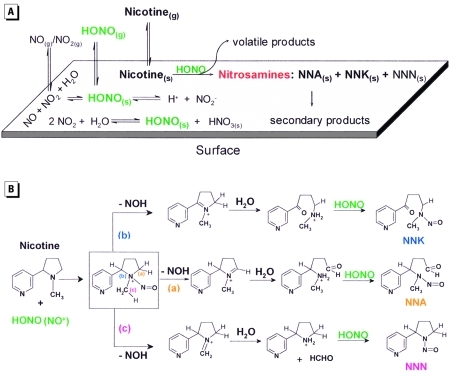
Figure 1.
Physical-chemical processes of nicotine reactions with nitrous acid on indoor surfaces. (A) Illustration of surface-mediated nitrosation of nicotine. (B) Proposed mechanism for the formation of TSNAs. Adapted from Sleiman et al. (2010b). Abbreviations: (a), proposed mechanism for formation of NNA; (b), proposed mechanism for formation of NNK; (c), proposed mechanism for the formation of NNN; (g), gas phase; HCHO, formaldehyde; (s), on surface; secondary products are those created by indoor chemical reactions from primary tobacco smoke products (e.g., NNK from nicotine).