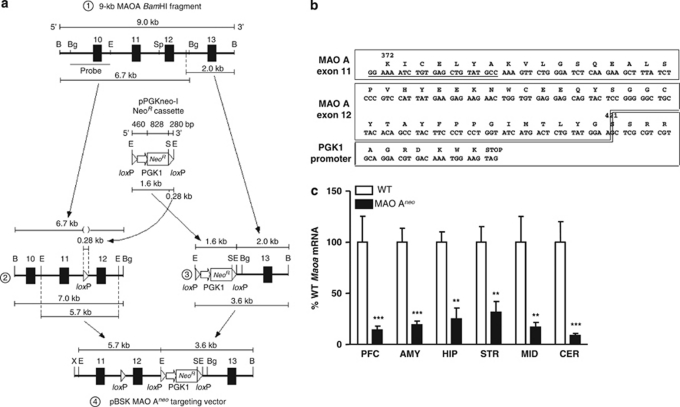
Figure 1.
Generation and transcript characterization of MAO-ANeo mice. (a) Construction of the MAO-ANeo targeting vector. (1) The 9.0-kb MAO-A BamHI fragment composed of a 6.7-kb BamHI–BglII and a 2.0-kb EcoRI–BamHI fragment. Unique SphI and EcoRI sites, within intron-11 and 12, respectively, were used for the insertion of loxP and NeoR cassettes. (2) The 0.28-kb SmaI–loxP–EcoRI fragment was embedded into the SphI site of a 6.7-kb BamHI–BglII fragment. (3) A 1.6-kb EcoRI floxed NeoR cassette was directionally ligated in the 5′-direction to a 2.0-kb EcoRI fragment containing exon-13. (4) A 5.7-kb EcoRI–BamHI fragment containing exon-11–loxP–exon-12 was cloned 5′ to the 3.6-kb floxed Neo-exon-13 fragment to complete the targeting vector. (b) Sequence of 210-bp PCR product and its deduced amino-acid sequence. (c) Quantification of WT Maoa mRNA levels in brain regions of MAO-ANeo mice. The values are represented as the mean±SEM. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with WT mice. Abbreviations: B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; S, SmaI; Sp, SphI; X, XhoI; PFC, prefrontal cortex; AMY, amygdala; HIP, hippocampus; STR, striatum; MID, midbrain; CER, cerebellum.