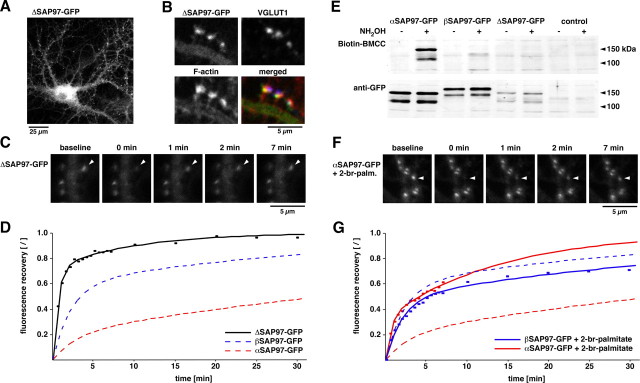
Figure 3.
Role of N-terminal domains for the kinetic properties of SAP97. A, Lentiviral expression of the deletion mutant ΔSAP97–EGFP in hippocampal neurons. B, Colocalization of ΔSAP97–EGFP with phalloidin (red) and VGLUT1 (blue). C, Images depicting fluorescence recovery of ΔSAP97–EGFP puncta. D, FRAP quantification of ΔSAP97–EGFP (black; n ≥ 13), αSAP97–EGFP (dashed red; data from Fig. 2 B), and βSAP97–EGFP (dashed blue; from Fig. 2 B). E, Western blot of HEK cell lysates from untransfected cells (control) and those transfected with α-, β-, or ΔSAP97–EGFP, probed with anti-GFP antibodies to detect total protein (bottom) or streptavidin-conjugated HRP to label Biotin-BMCC [1-biotinamido-4-(4′-[maleimidoethyl-cyclohexane]-carboxamido) butane] (top). Only αSAP97–EGFP is biotinylated after hydroxylamine (NH2OH) treatment, indicating palmitoylation of its N-terminal cysteine residues. F, Images depicting fluorescence recovery of αSAP97–EGFP in the presence of 2-bromopalmitate. G, FRAP curves of α- and βSAP97–EGFP plus 2-bromopalmitate (red solid, n = 23; blue solid, n = 28, respectively), or untreated (dashed lines; same data as D and Fig. 2 B).