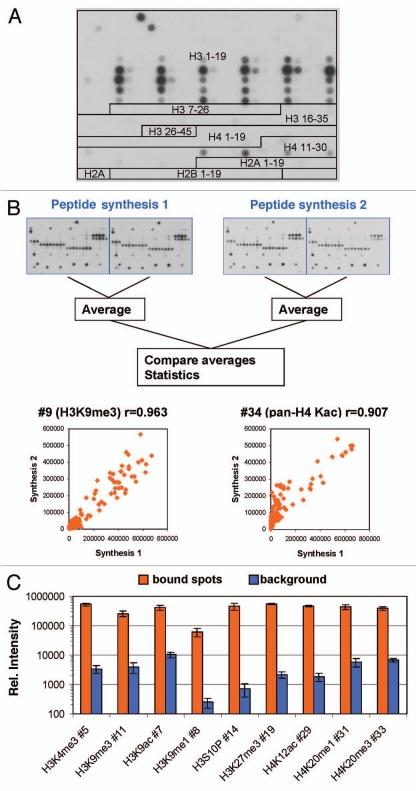
Figure 1.
(A) Design of the peptide array used in this study (detailed information on the sequence and modification of each peptide is given in Sup. Table 1). Here the image obtained with antibody #1 is used for illustration. (B) Antibody binding to independently synthesized peptides. Spot intensities were averaged from the two internal repeats of the array and compared between arrays that were synthesized independently. One image obtained with H3K4me3 is chosen for illustration. The scatter plots show a comparison of the intensity of peptide binding in both arrays. The r value refers to the Pearson correlation coefficient of both intensities. (C) Reproducibility of peptide binding intensities between different peptides on the same array. For several antibodies, the binding intensities to all peptides containing the primary epitope (after exclusion of false negatives) were averaged and plotted in log scale (orange columns, the error bars display the standard deviations). As background, binding intensities to the 100 weakest spots were used (blue columns, the error bars display the standard deviations). For antibody numbers cf. Supplemental Table 2.