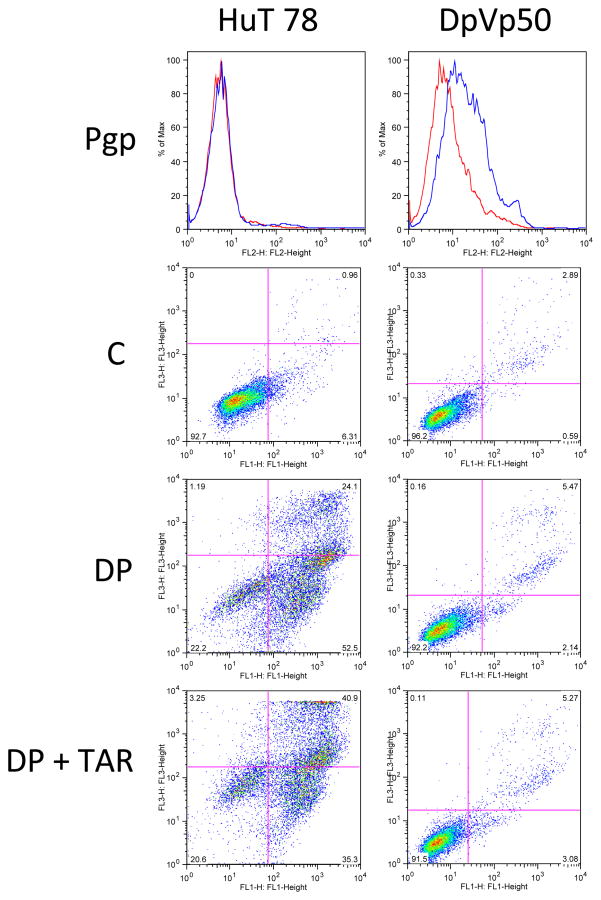
Figure 4.
Resistance to romidepsin is not mediated by Pgp expression in HuT78 DpVp50 cells. HuT78 parental and DpVp50 cells were incubated with the Pgp-specific antibody, MRK-16 (blue histogram), or IgG negative control antibody (red histogram) for 30 min after which cells were washed and incubated with phycoerythrin-labeled secondary antibody (top row, Pgp). While HuT78 parental cells are Pgp negative, the DpVp50 cells express low but detectable levels. Cells were also left untreated (second row, C) or were incubated with 50 ng/mL romidepsin for 48 h in the presence (third row, DP) or absence (bottom row DP + TAR) of 250 nM of the Pgp inhibitor tariquidar, after which cells were incubated with annexin V antibody and propidium iodide. Cells in the lower left quadrant are viable cells, while cells in the lower right quadrant are early apoptotic cells, and cells in the upper right quadrant are late apoptotic or necrotic cells. HuT parental cells readily undergo apoptosis after incubation with romidepsin either in the presence or absence of tariqudiar, so shown by the increase of cells in the upper and lower right quadrants. DpVp50 cells are resistant to romidepsin whether the inhibitor is added or not, suggesting a resistance mechanism that does not involve Pgp.