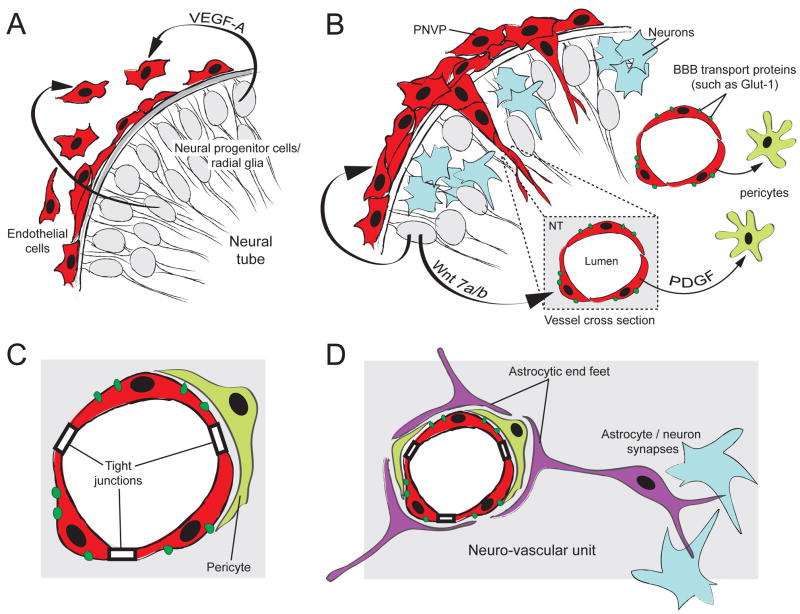
Figure 2. Model of early BBB and neuro-vascular unit formation.
(A) Neural progenitor cells (grey) secrete VEGF-A to recruit ECs to the surface of the neural tube. VEGF-A signaling from the neural tube is also required for subsequent blood vessel ingression into the neural tube (not shown). (B) At the onset of neurogenesis (differentiated neurons in blue), blood vessel sprouts originating from the PNVP invade the neural tube, forming the INVP. Wnt7 signaling is required for proper blood vessel ingression and induction of BBB-specific membrane transport proteins (such as Glut-1). Blood vessels recruit pericytes (light green) via the PDGF-B signaling pathway. (C) Pericyte recruitment is essential for stabilization of the BBB and for maintenance of tight junctions and Glut-1 expression. Pericytes are an important component of the neuro-vascular unit. (D) At the onset of gliogenesis, astrocytes (purple) differentiate and project cellular processes called end -feet to wrap around the CNS blood vessels. Astrocytes also form synaptic complexes with neurons. While some components of the BBB and the neuro-vascular unit develop before astrocytes differentiate, astrocytes are required for stabilization of the BBB and are critical components of the neuro-vascular unit.