Fig. 5.
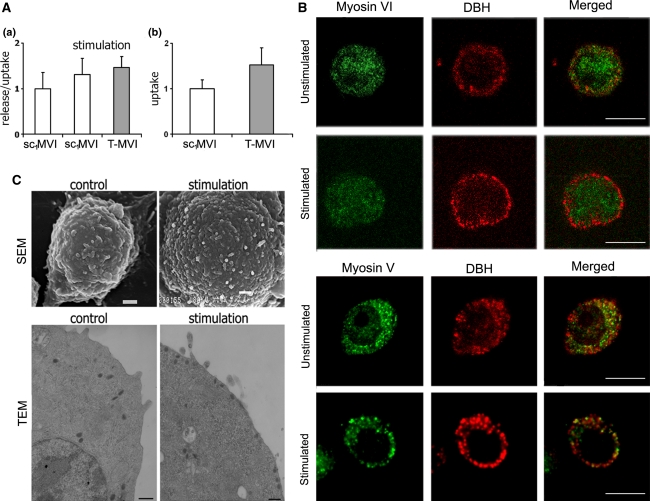
MVI is not crucial for catecholamine secretion. A Influence of MVI knockdown on secretion (a) and uptake (b) of noradrenaline (NA) in T-MVI and control sc1MVI cells. These values (presented as means ± SD) were calculated based on the radioactive noradrenaline ([3H[NA]) measurements in the samples, as described in “Materials and methods”. (a) Secretion stimulated with 56 mM KCl is presented as the ratio of release (amount of radioactivity released to the medium) to uptake, and is referred to non-stimulated both control sc1MVI and knocked down (T-MVI) cells; (b) uptake reflects the amount of radioactivity incorporated into the cells and is a sum of the radioactivity both released to the medium and remained in the cells (control, sc1MVI) and (T-MVI). B Distribution of MVI and MV in PC12 cells before and after 10-min stimulation with 56 mM KCl. Both myosins (in green) were stained with the respective antibodies and chromaffin granules (red) with anti-dopamine β-hydroxylase antibody. These are the 0.8 μm images of cell center attained with Leica TCS SP2 spectral confocal microscope equipped with HCX PL APO 63x/1.25-0.75 Oil Cs objective. Other details as described under “Materials and methods” section. Bars 10 μm. C Morphology of unstimulated and 10-min stimulated PC12 cells. Micrographs were attained with scanning (SEM) and transmission (TEM) electron microscopes as described under “Materials and methods” section. Bars 1 μm in SEM and 200 nm in TEM