Fig. 1. Activation of LXR in transgenic mice conferred resistance to APAP hepatotoxicity.
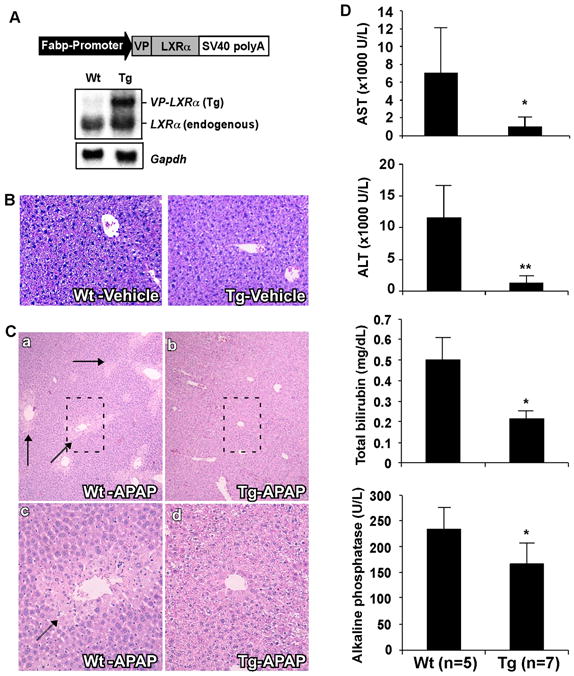
(A) Schematic representation of the Fabp-VP-LXRα transgene and confirmation of transgene expression by Northern blot analysis. Membrane was probed with a LXRα cDNA probe. Each lane represents RNA samples pooled from five mice of the same genotype. Fabp, rat fatty acid binding protein; SV40, SV40 poly(A) sequences; Tg, transgenic; VP, viral protein 16; Wt, wild type. (B) Representative H&E staining on liver paraffin sections of the vehicle-treated mice. (C) Representative H&E staining on liver paraffin sections of APAP-treated mice. APAP-induced centrilobular necrosis is indicated by arrows. C-c and C-d are higher magnifications of the framed fields in C-a and C-b, respectively. (D) Serum levels of AST, ALT, total bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase in mice treated with APAP. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.
