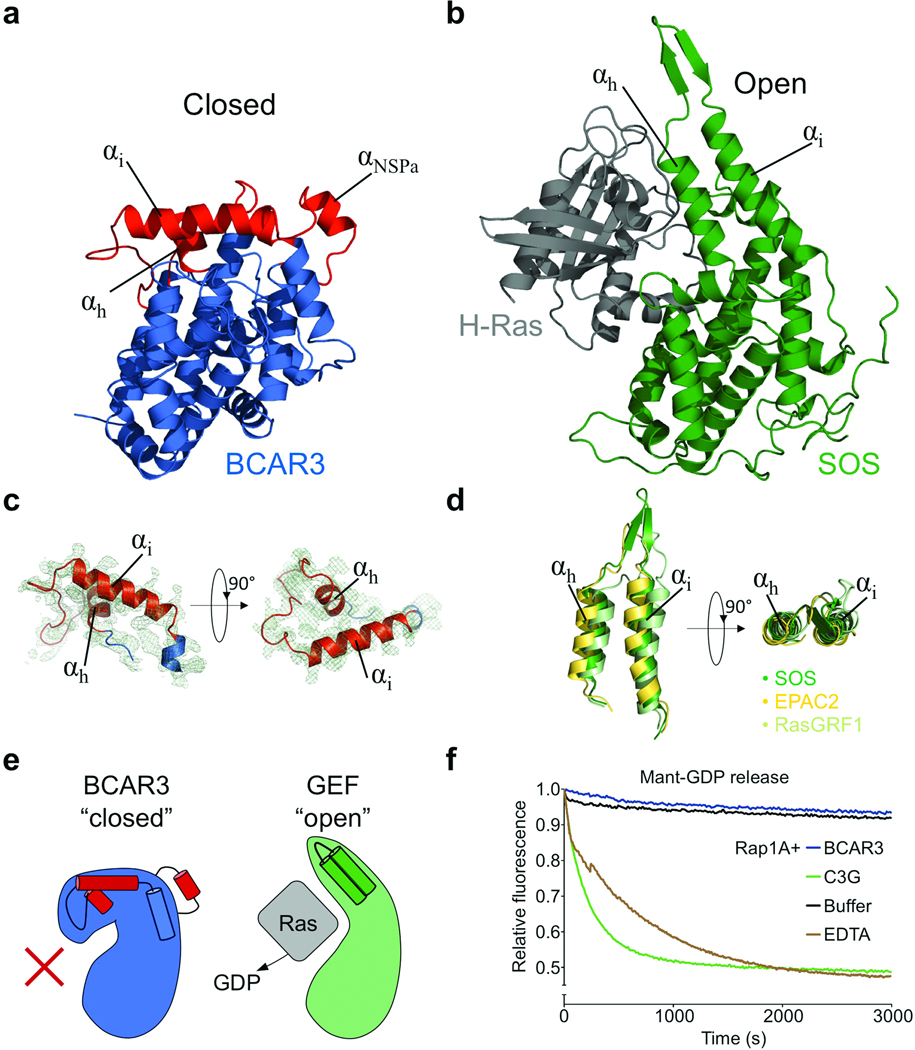
Figure 1.
The BCAR3 C-terminal domain resembles a Cdc25-homology domain but adopts a closed conformation incapable of canonical GEF function. (a) Structure of the BCAR3 Cas interaction domain. The C-terminal domain of the NSP BCAR3 overall adopts a Cdc25 homology domain fold (blue) yet crucial regions (red) are altered when compared with the prototypical Cdc25-homology domain of Ras GEFs. Also indicated in red is additional helix αNSPa in a region unique to NSP proteins. (b) SOS in complex with Ras. SOS (green) adopts an open conformation accommodating its target GTPase Ras (grey; PDBid:1bkd)17. (c) Structure of the closed “helical hairpin” in BCAR3 with the 2Fo-Fc electron density map (contoured to 1 σ) displayed from two orthogonal directions. (d) The helical hairpins of SOS, EPAC and RasGRF1. Orientations are identical to those used in panel c. (e) Schematic illustrating conformations of “closed” BCAR3 compared to a canonical “open” GEF conformation. The canonical GTPase interaction site is occluded in the “closed” Cdc25-homology domain of BCAR3 rendering it incapable of canonical GEF function. (f) The Cdc25-homology domain of BCAR3 shows no GEF activity in vitro, tested by comparing the release of mant-GDP from Rap1A, a putative GTPase target for BCAR3, in the presence of BCAR3, C3G, or EDTA.