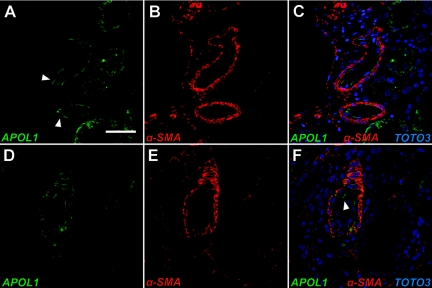
Figure 4.
De novo localization of APOL1 to the renal arterial wall in FSGS. Confocal immunofluorescence imaging of medium sized renal arterioles from the normal human kidney (A–C) and from FSGS (D–F). (A & C, green) APOL1 signal is identified in cells anatomically consistent with endothelium of medium-sized renal arterioles (arrowheads) in the normal adult human kidney and adjacent tubular segments but does not colocalize with vascular smooth muscle cells of renal arterioles stained with anti-α-SMA antibody (B & C, red). APOL1-positive cells are located in the luminal wall of the blood vessel with surrounding α-SMA positive vascular smooth muscle cells, consistent with endothelial localization. (D & F, green) Representative cross-section of a renal arteriole from an FSGS biopsy demonstrates persistent endothelial APOL1 signal and de novo appearance within the vessel wall compared with the normal arteriole (A). (E & F, red) Anti-α-SMA antibody staining identifies APOL1-positive cells as vascular smooth muscle (F, green). The vascular endothelium remains positive for APOL1 staining (arrowhead). (C & F, blue) Nuclei were visualized with TOTO-3 staining. Scale bars: 50 μm (A–F).