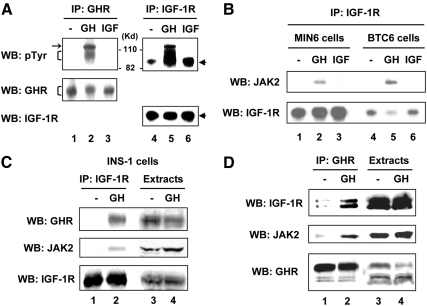
Fig. 2.
GH specifically induces formation of GHR-JAK2-IGF-IR protein complex in β-cells. A, GH-induced phosphoprotein complex in the anti-IGF-IR precipitates. Serum-starved MIN6 cells were stimulated with vehicle (−), bGH (500 ng/ml), or IGF-I (20 ng/ml) for 15 min. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-GHR (lanes 1–3) or anti-IGF-IR (lanes 4–6). The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-pTyr (lanes 1–6), anti-GHR (lanes 1–3), or anti-IGF-IR (lanes 4–6). The GHR, JAK2, and IGF-IR bands are indicated by the bracket, arrow, and arrowhead, respectively. WB, Western blot. B, JAK2 is a component of the GH-induced protein complex from the anti-IGF-IR precipitates. MIN6 and BTC6 cells treated as in A were subjected to IP with anti-IGF-IR antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-JAK2 and anti-IGF-IR, respectively. C, GHR is also a component of the GH-induced protein complex from the anti-IGF-IR precipitates. Serum-starved INS-1 cells were stimulated with vehicle (−) or bGH (500 ng/ml) for 15 min. Cell extracts were subjected to IP with anti-IGF-IR followed by immunoblotting (lanes 1 and 2) or direct immunoblotting (lanes 3 and 4) with anti-GHR, anti-JAK2, and anti-IGF-IR, respectively. D, Reverse coimmunoprecipitation experiment. INS-1 cells as treated in C were subjected to IP with anti-GHR followed by immunoblotting (lanes 1 and 2) or direct immunoblotting (lanes 3 and 4) with anti-IGF-IR, anti-JAK2, and anti-GHR, respectively.