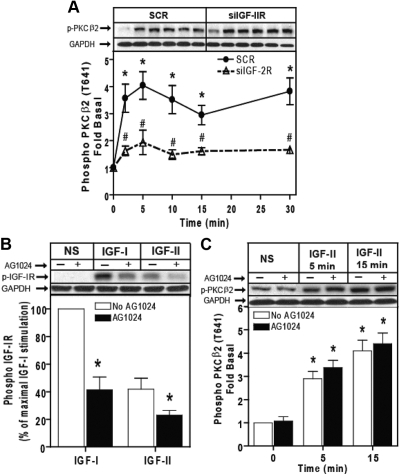
Fig. 6.
IGF-II/M6P receptor mediates IGF-II-stimulated PKCβ2 phosphorylation. A, Serum-starved HEK293 cells were transfected with control scrambled siRNA (SCR) or siRNA targeting the IGF-II/M6P receptor (siIGF-2R) for 48 h were stimulated with 10 nm IGF-II for the indicated times, and activation of PKCβ2 in whole-cell lysate samples was determined by immunoblotting with phosphorylation state-specific IgG. PKCβ2 phosphorylation is expressed as fold increase above the basal level in NS cells. A representative phospho-PKCβ2 and basal GAPDH immunoblots are shown above a bar graph depicting mean ± sd for three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 vs. nonstimulated (NS); #, P < 0.05 vs. scrambled (SCR) treated. B, Serum-deprived cells were preincubated with 1 μm AG1024 for 15 min before stimulation with 10 nm IGF-I and 10 nm IGF-II for 10 min. Basal (NS), IGF-I-stimulated, and IGF-II-stimulated IGF-I receptor β-subunit phosphorylation was determined as described. The change in IGF-I receptor phosphorylation is expressed as the percentage of maximal stimulation. p-IGF-1R, phosphorylated IGF-1R. C, Serum-starved HEK293 cells were pretreated with 1 μm AG1024 for 15 min before stimulation with 10 nm IGF-II for the indicated times, and activation of PKCβ2 in whole-cell lysate samples was determined by immunoblotting with phosphorylation state-specific IgG. PKCβ2 phosphorylation is expressed as fold increase above the basal level in NS cells. A representative phospho-PKCβ2 and basal GAPDH immunoblots are shown above a bar graph depicting mean ± sd for three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 vs. nonstimulated (NS).