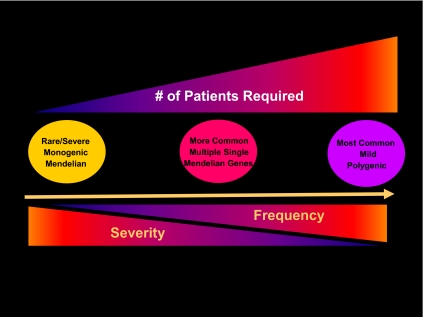
Fig. 1.
The genetic architecture of the endocrine disorders. Whereas monogenic disorders are rare, they typically have a high impact as seen on the left end of the spectrum. Oligogenic disorders represent interactions of a small number of Mendelian genes that interact to produce a more complex phenotypic spectrum of gene expression. On the right is the polygenic nature of most common genetic disorders in which mutations in several genes, each mild in its impact and fairly frequent in their incidence, act collectively to produce a disease that is common.